P2645
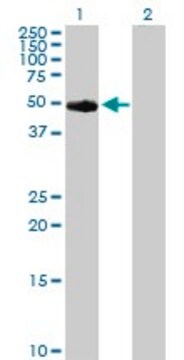
Protein Kinase A Catalytic Subunit from bovine heart
≥9 units/μg protein (cyclic-AMP is not required for this activity), lyophilized (white powder to sticky mass to hard pellet)
Sinônimo(s):
PKA
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352204
eCl@ss:
32160410
NACRES:
NA.32
Produtos recomendados
forma
lyophilized (white powder to sticky mass to hard pellet)
Nível de qualidade
atividade específica
≥9 units/μg protein (cyclic-AMP is not required for this activity)
peso molecular
40,862 Da
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
Descrição geral
Protein Kinase A enzyme is composed of two subunits- catalytic and regulatory. The catalytic subunit exists as a monomer in the presence of cAMP and has a molecular weight of 40,862 Da.
Aplicação
Protein Kinase A (PKA) Catalytic Subunit from bovine heart has been used-
- to study PKA-mediated inhibition of IRK1 (inwardly rectifying K+) channels
- in in Vitro PKA pPhosphorylation assay
- in Vitro affinity binding assays
- to study effects of PKA on inspiratory drive currents in functionally active motorneurons
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Protein Kinase A (PKA) controls the transduction of Hedgehog signaling and participates in proliferation and fate specification. It phosphorylates several neurotransmitter receptors, transcription factors and constituents of various intracellular signaling pathways.
Protein Kinase A catalyzes the transfer of terminal phosphate from ATP to threonine or serine residues present on various proteins. This protein is inactive in the absence of cAMP, where the catalytic and regulatory subunits are bound together. The regulatory subunit, in the presence of cAMP, binds to cAMP and releases the catalytic subunit.
Embalagem
Package size based on phosphorylating units
Definição da unidade
Phosphorylating Activity: One unit will transfer 1.0 picomole phosphate from ATP to hydrolyzed and partially dephosphorylated casein per minute at pH 6.5 at 30°C, determined by measuring the production of ADP.
forma física
Lyophilized powder with sucrose and phosphate buffer salts as stabilizer.
Nota de preparo
Prepared from protein kinase A (P 5511)
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Please note that the pack size has been changed to align with the unit definition, while the number of phosphorylating units remain the same as before.
inibidor
Nº do produto
Descrição
Preços
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Cyclic nucleotides in the nervous system
Basic Neurochemistry, 423-441 (2012)
F T Hartl et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 258(6), 3950-3955 (1983-03-25)
The physical and chemical properties of purified catalytic and regulatory subunits of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine brain, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle were compared. The catalytic subunits from all three sources were identical with respect to molecular
Ken Tougane et al.
Plant physiology, 152(3), 1529-1543 (2010-01-26)
Abscisic acid (ABA) is postulated to be a ubiquitous hormone that plays a central role in seed development and responses to environmental stresses of vascular plants. However, in liverworts (Marchantiophyta), which represent the oldest extant lineage of land plants, the
Christopher M Bocchiaro et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 23(4), 1099-1103 (2003-02-25)
Plasticity underlying adaptive, long-term changes in breathing behavior is hypothesized to be attributable to the modulation of respiratory motoneurons by intracellular second-messenger cascades. In quiescent preparations, protein kinases, including cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), potentiate glutamatergic inputs. However, the dynamic
E Wischmeyer et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 93(12), 5819-5823 (1996-06-11)
Strongly rectifying IRK-type inwardly rectifying K+ channels are involved in the control of neuronal excitability in the mammalian brain. Whole-cell patch-clamp experiments show that cloned rat IRK1 (Kir 2.1) channels, when heterologously expressed in mammalian COS-7 cells, are inhibited following
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica