Kluczowe dokumenty
919381
CCW16
≥95%
Synonim(y):
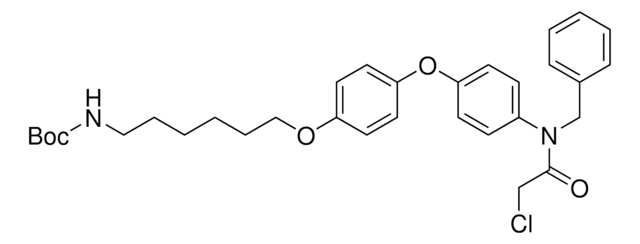
N-benzylo-2-chloro-N-(4-(4-metoksyfenoksy)fenylo)acetamid, Ligand celujący w RNF4, Ligand dla badań 11779, Ligand ligazy ubikwityny E3
About This Item
Polecane produkty
ligand
CCW16
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥95%
Formularz
powder
przydatność reakcji
reagent type: ligand
grupa funkcyjna
amine
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
ciąg SMILES
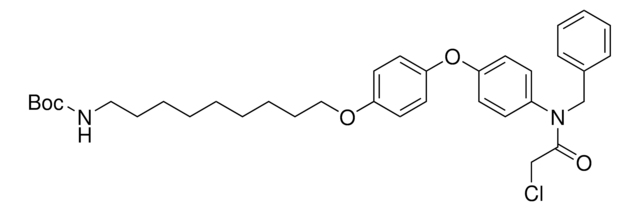
COC1=CC=C(OC2=CC=C(N(CC3=CC=CC=C3)C(CCl)=O)C=C2)C=C1
InChI
1S/C22H20ClNO3/c1-26-19-11-13-21(14-12-19)27-20-9-7-18(8-10-20)24(22(25)15-23)16-17-5-3-2-4-6-17/h2-14H,15-16H2,1H3
Klucz InChI
DPADEQNOMBTITM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Powiązane kategorie
Zastosowanie
Inne uwagi
Portal: Budowa 11779 degraderów do ukierunkowanej degradacji białek
Covalent Ligand Screening Uncovers a RNF4 E3 Ligase Recruiter for Targeted Protein Degradation Applications
Targeted Protein Degradation by Small Molecules
Small-Molecule PROTACS: Nowe podejścia do degradacji białek
Ukierunkowana degradacja białek: od biologii chemicznej do odkrywania leków
Informacje prawne
produkt powiązany
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Dokumenty section.
Proszę o kontakt, jeśli potrzebna jest pomoc Obsługa Klienta
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 919381-100MG | 4065265338998 |
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej