F0162
Fibronectina
lyophilized powder, 45 kDa
Sinônimo(s):
Fibronectin
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
human plasma
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Formulário
lyophilized powder
peso molecular
45 kDa
embalagem
pkg of 0.5 mg
técnica(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Impurezas
HIV and HBsAg, source material tested negative
Small proteolytic fragments, may contain traces
solubilidade
water: soluble ≥0.500 mg/mL, clear to slightly hazy, colorless
nº de adesão UniProt
Condições de expedição
wet ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
Informações sobre genes
human ... FN1(2335)
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
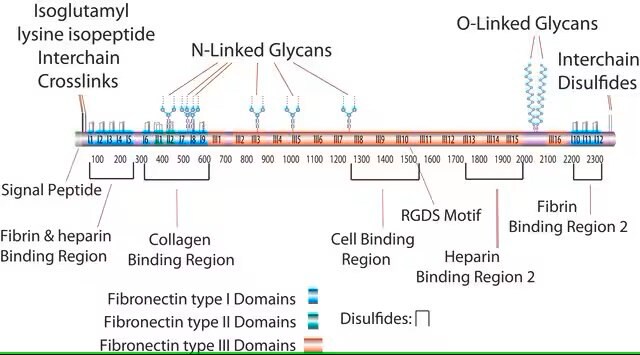
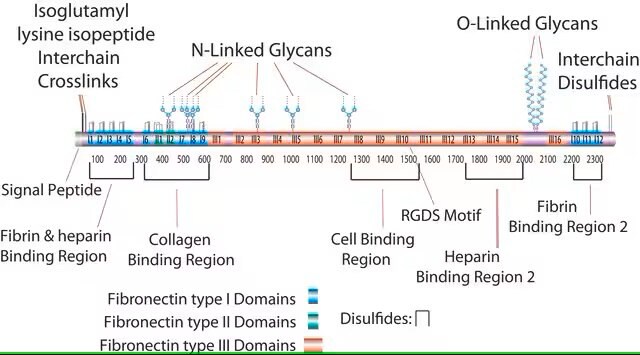
This fragment has an acidic pI (4.9-5.3) and does not bind to heparin. This domain is resistant to proteolysis due to intrachain disulfide bonding and the attached carbohydrate. The intrachain disulfide bonds are essential for binding to gelatin, while the complex, branched, asparagine-linked carbohydrate is not. This fragment binds to C1q, but not to fibrin.
Atenção
Nota de preparo
recomendado
Palavra indicadora
Warning
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Órgãos-alvo
Respiratory system
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Extracellular matrix proteins such as laminin, collagen, and fibronectin can be used as cell attachment substrates in cell culture.
Protocolos
Dilute fibronectin to the desired concentration. Optimum conditions for attachment are dependent on cell type and application. The typical coating concentration is 1 – 5 ug/cm2.Fibronectin coating protocol, products, and FAQs at sigmaaldrich.com
Dilute fibronectin to the desired concentration. Optimum conditions for attachment are dependent on cell type and application. The typical coating concentration is 1 – 5 ug/cm2.Fibronectin coating protocol, products, and FAQs.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica