T11509
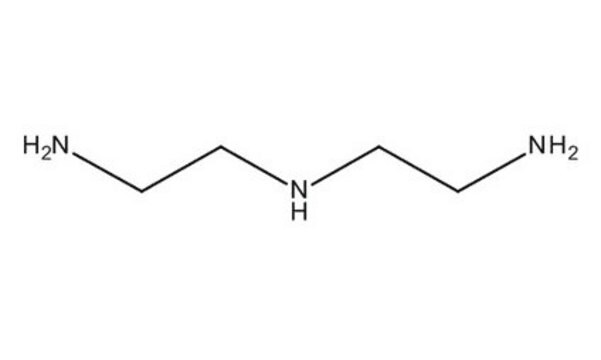
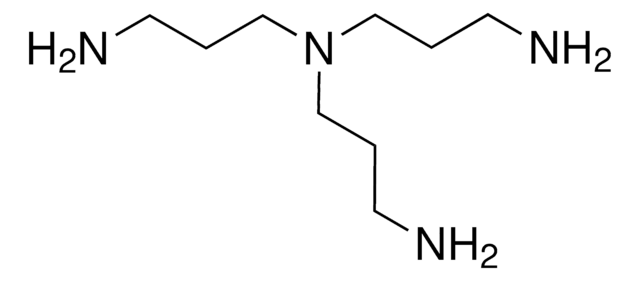
Tetraethylenepentamine
technical grade
Sinônimo(s):
TEPA, Tetrene
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
grau
technical grade
Nível de qualidade
densidade de vapor
6.53 (vs air)
pressão de vapor
<0.01 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Ensaio
≥30%
Formulário
viscous liquid
temperatura de autoignição
610 °F
índice de refração
n20/D 1.505 (lit.)
p.e.
340 °C
pf
−40 °C (lit.)
densidade
0.998 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
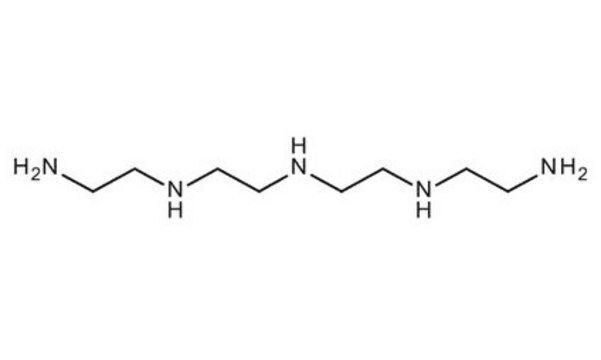
NCCNCCNCCNCCN
InChI
1S/C8H23N5/c9-1-3-11-5-7-13-8-6-12-4-2-10/h11-13H,1-10H2
chave InChI
FAGUFWYHJQFNRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- To functionalize magnesium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate (Mg-MOF-74) to enhance the CO2 adsorption performance of the material.
- To modify magnetic chitosan resin to form amine-bearing chitosan for the efficient removal of uranium from an aqueous solution.
- To synthesize poly(vinyl-chloride)/tetraethylenepentamine (PVC-TEPA) composite material, which is used as an efficient catalyst for the Knoevenagel condensation reaction.
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B - Skin Sens. 1
Código de classe de armazenamento
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 2
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
325.4 °F - closed cup
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
163 °C - closed cup
Equipamento de proteção individual
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica