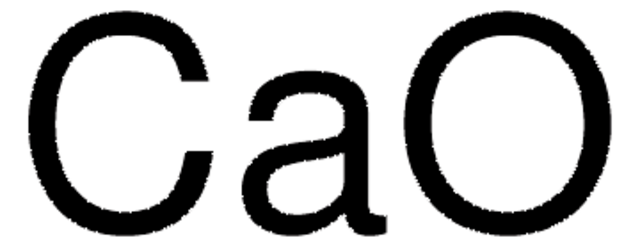Kluczowe dokumenty
645613
Sodium oxide
80%
Synonim(y):
Disodium monoxide, Disodium oxide
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Próba
80%
Formularz
solid
przydatność reakcji
core: sodium
reagent type: catalyst
zanieczyszczenia
~20% Na2O2
gęstość
2.27 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
ciąg SMILES
[O--].[Na+].[Na+]
InChI
1S/2Na.O/q2*+1;-2
Klucz InChI
KKCBUQHMOMHUOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Eye Dam. 1 - Ox. Sol. 1 - Skin Corr. 1A
Kod klasy składowania
5.1A - Strongly oxidizing hazardous materials
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej