Kluczowe dokumenty
381462
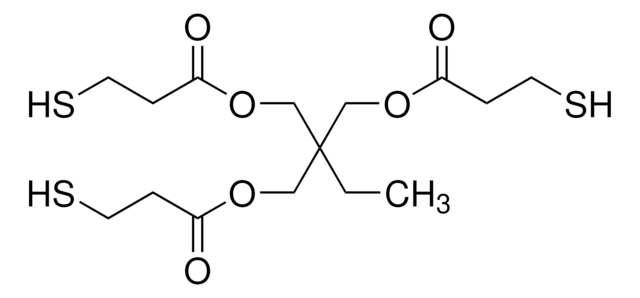
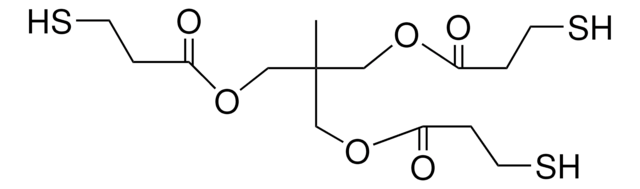
Pentaerythritol tetrakis(3-mercaptopropionate)
>95%
Synonim(y):
Pentaerythritol (3-mercaptopropionate), Pentaerythritol terakis(3-mercaptopropionate), Pentaerythritol tetra(3-mercaptopropionate)
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
Próba
>95%
współczynnik refrakcji
n20/D 1.531 (lit.)
bp
275 °C/1 mmHg (lit.)
gęstość
1.28 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
ciąg SMILES
SCCC(=O)OCC(COC(=O)CCS)(COC(=O)CCS)COC(=O)CCS
InChI
1S/C17H28O8S4/c18-13(1-5-26)22-9-17(10-23-14(19)2-6-27,11-24-15(20)3-7-28)12-25-16(21)4-8-29/h26-29H,1-12H2
Klucz InChI
JOBBTVPTPXRUBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Zastosowanie
- Polymeric degradable networks through thiol-ene click reactions with tri/tetra-acrylates.
- Thiol-ene-methacrylate composites, which are applicable as dental restorative materials.
- Network solid polymer electrolytes based on polydimethylsiloxane, for lithium-ion batteries.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
The Progress in Development of Dental Restorative Materials
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej