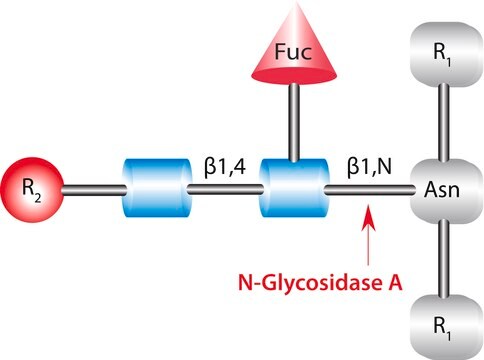
N8271
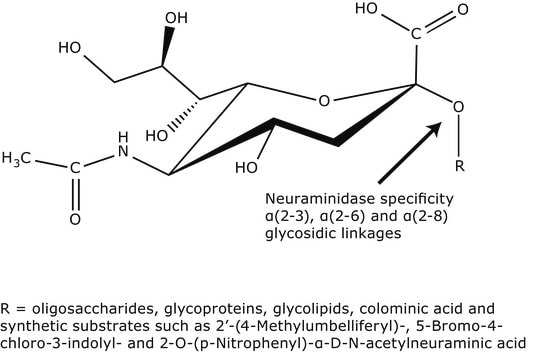
α(2→3,6,8,9) Neuraminidase from Arthrobacter ureafaciens
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution
Sinônimo(s):
Neuraminidase from Arthrobacter ureafaciens, Acyl-neuraminyl Hydrolase, Sialidase
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
recombinante
expressed in E. coli
Nível de qualidade
forma
buffered aqueous solution
atividade específica
≥135 units/mg protein
peso molecular
88 kDa
95 kDa
atividade externa
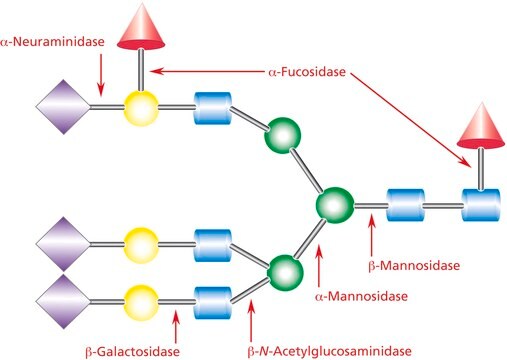
β-Galactosidase, α-mannosidase, β-hexosaminidase, α-fucosidase, and proteases, none detected
Condições de expedição
wet ice
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Embalagem
Definição da unidade
forma física
Nota de preparo
Código de classe de armazenamento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica