W265501
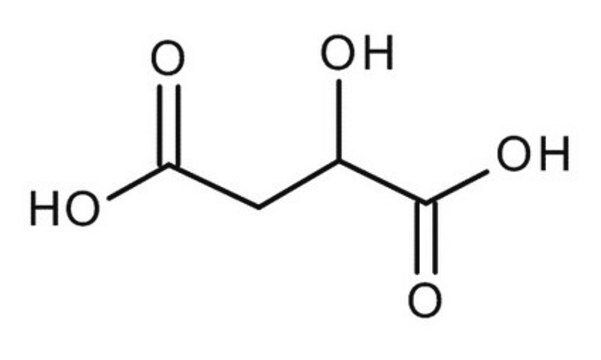
DL-Malic acid
99%
Sinônimo(s):
(±)-2-Hydroxysuccinic acid, DL-Hydroxybutanedioic acid
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
synthetic
Nível de qualidade
grau
Kosher
conformidade reg.
FDA 21 CFR 1084.1069
FDA 21 CFR 117
densidade de vapor
4.6 (vs air)
pressão de vapor
<0.1 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Ensaio
99%
temperatura de autoignição
644 °F
pf
131-133 °C (lit.)
solubilidade
H2O: soluble 646.6 g/L at 20 °C
aplicação(ões)
flavors and fragrances
Documentação
see Safety & Documentation for available documents
alérgeno alimentar
no known allergens
Organoléptico
odorless
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
OC(CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H6O5/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2,5H,1H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)
chave InChI
BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- Tetra-Ln(3+)-Implanted Tellurotungstates Covalently Modified by dl-Malic Acid: Proton Conduction and Photochromic Properties.: This innovative study showcases dl-Malic acid as a key component in the synthesis of advanced tellurotungstates, contributing to notable enhancements in proton conduction and photochromic properties, which are critical for applications in smart materials and sensors (Niu et al., 2024).
- Direct regeneration of spent LiFePO(4) materials via a green and economical one-step hydrothermal process.: dl-Malic acid is utilized in a green chemistry approach for the direct regeneration of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) materials, demonstrating a sustainable pathway for battery recycling and highlighting its importance in promoting environmental sustainability (Yang et al., 2023).
- Chitin Extracted from the Shell of Blue Swimming Crabs (Portunus pelagicus Linn.) Inhibits NF-kappaB p65 in Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcerative Wistar Rats.: In this research, dl-Malic acid serves as a catalyst in the extraction and functional activity testing of chitin, which is shown to have significant anti-inflammatory effects, suggesting its potential in pharmaceutical applications (Amelia et al., 2023).
- Manganese-Titanium Mixed Ion Sieves for the Selective Adsorption of Lithium Ions from an Artificial Salt Lake Brine.: Highlighting the application of dl-Malic acid in the synthesis of ion-exchange materials, this study points towards its utility in enhancing the selective adsorption properties of manganese-titanium mixed ion sieves, crucial for lithium recovery from brines (Ding et al., 2023).
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Palavra indicadora
Warning
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Eye Irrit. 2
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
397.4 °F
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
203 °C
Equipamento de proteção individual
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| W265501-10KG | |
| W265501-10KG-K | 4061834396789 |
| W265501-5KG | |
| W265501-SAMPLE | |
| W265501-1KG | |
| W265501-1KG-K | 4061835565740 |
| W265501-5KG-K | 4061834396796 |
| W265501-SAMPLE-K | 4061834355496 |
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica