Kluczowe dokumenty
42602
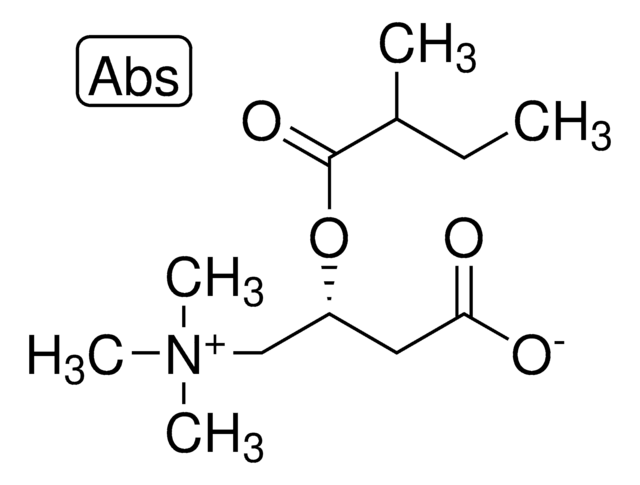
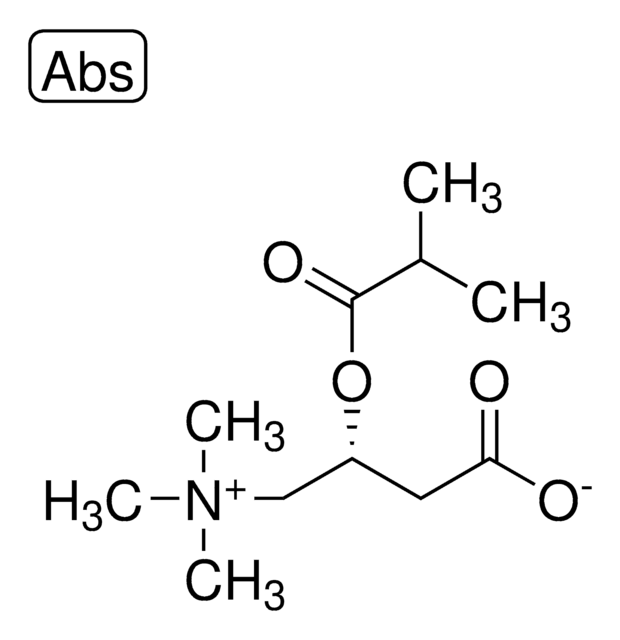
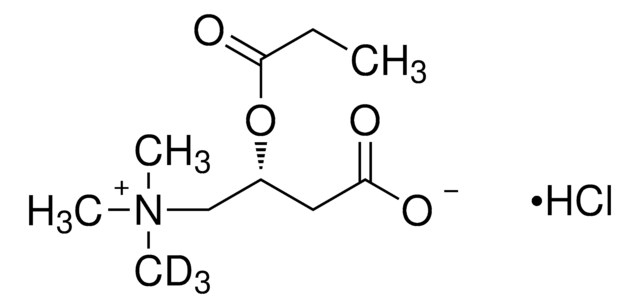
Propionyl-L-carnitine
≥94.0% (HPLC), suitable for LC/MS
Synonim(y):
(2R)-3-Carboxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-2-(1-oxopropoxy)-1-propanaminium inner salt, L-Carnitine propionyl ester, C3-Carnitine, Propanoyl-L-carnitine
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Nazwa produktu
Propionyl-L-carnitine, ≥94.0% (HPLC)
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥94.0% (HPLC)
Formularz
powder or crystals
aktywność optyczna
[α]/D -23±3°, c = 1 in H2O
metody
LC/MS: suitable
zanieczyszczenia
≤10% water (calcd. from elemental analysis)
kolor
white to off-white
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
ciąg SMILES
[O-]C(C[C@@H](OC(CC)=O)C[N+](C)(C)C)=O
InChI
1S/C10H19NO4/c1-5-10(14)15-8(6-9(12)13)7-11(2,3)4/h8H,5-7H2,1-4H3/t8-/m1/s1
Klucz InChI
UFAHZIUFPNSHSL-MRVPVSSYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej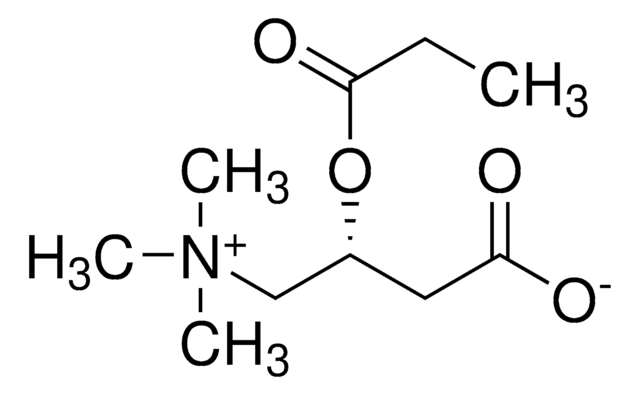
![[(3R)-3-Hydroxybutyryl]-L-carnitine analytical standard](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/658/500/ff9570f8-a346-4077-9983-d0e67400bf47/640/ff9570f8-a346-4077-9983-d0e67400bf47.png)