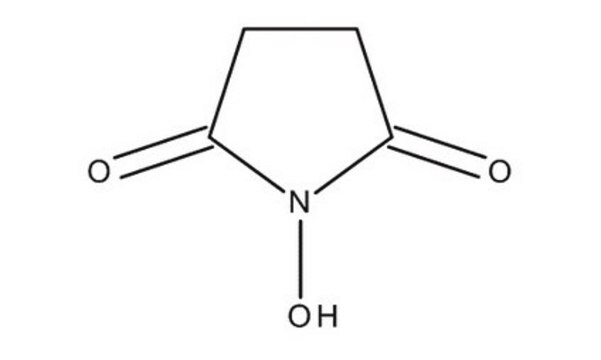
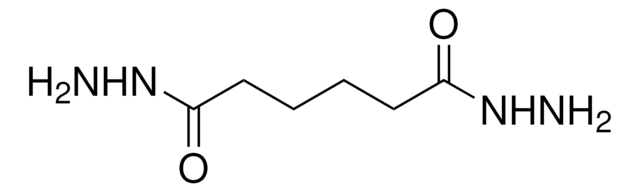
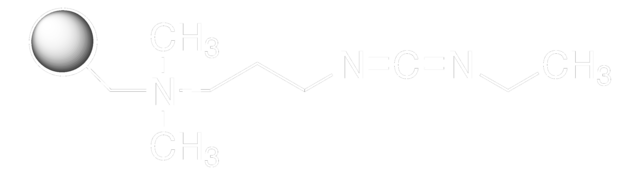
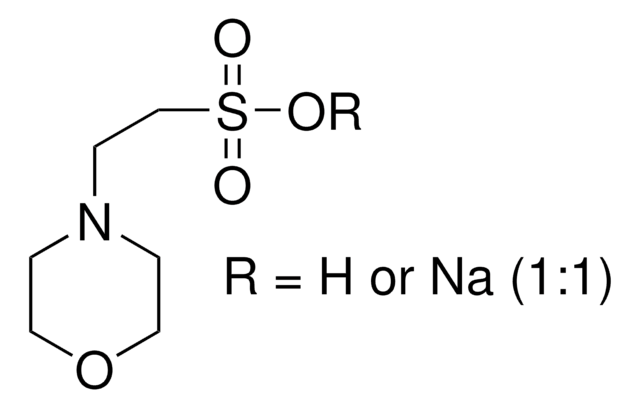
Key Documents
E7750
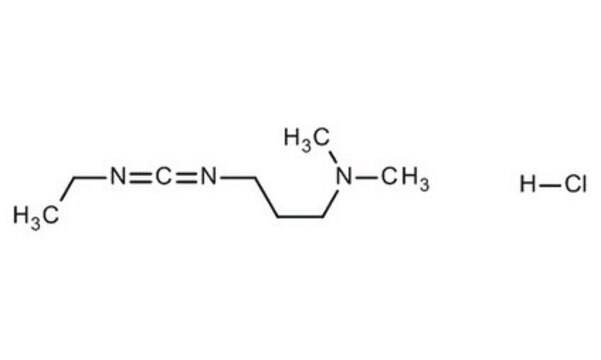
N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
commercial grade, powder
Synonim(y):
N-Ethyl-N′-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, EDAC, EDC, EDC hydrochloride, WSC hydrochloride
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
klasa czystości
commercial grade
Postać
powder
metody
Northern blotting: suitable
bioconjugation: suitable
kolor
white to off-white
mp
110-115 °C (lit.)
rozpuszczalność
H2O: ≤100 mg/mL
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
ciąg SMILES
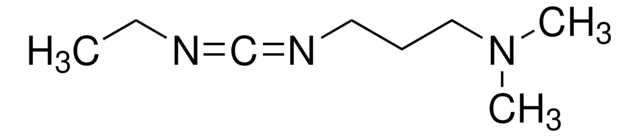
Cl.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C
InChI
1S/C8H17N3.ClH/c1-4-9-8-10-6-5-7-11(2)3;/h4-7H2,1-3H3;1H
Klucz InChI
FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
The versatility of EDC HCl further manifests in its capacity to modify nucleic acids, allowing for the labeling of DNA and RNA through their 5′ phosphate groups. This functionality enhances the visualization, tracking, and analysis of these crucial molecules, contributing significantly to the progression of nucleic acid research. Moreover, EDC HCl serves as a vital biomolecule bridge, acting as a crosslinker that connects amine-reactive NHS-esters of biomolecules to carboxyl groups. This technique is particularly valuable in protein conjugation, enabling the creation of hybrid molecules with novel properties and functions. The underlying mechanism of EDC HCl involves its reaction with a carboxyl group, forming an unstable intermediate that actively seeks an amine partner. The delicate balance of this reaction emphasizes the need for optimizing conditions to ensure efficient conjugation. The assistance of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) further enhances EDC HCl′s capabilities by stabilizing the intermediate and enabling two-step conjugation procedures, offering greater flexibility and control, especially when dealing with complex biomolecules.
Zastosowanie
- N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride has been used for the formation of FND (fluorescent nanodiamonds)-transferrin bioconjugates.
- It has been used for crosslinking polyethylenimine to gold particles.
- It has been used as a carbodiimide linkage agent for coating of carboxylated polystyrene beads with biotinylated BSA (bovine serum albumin).
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Cechy i korzyści
Inne uwagi
najczęściej kupowane z tym produktem
produkt podobny
produkt powiązany
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Organy docelowe
Stomach,large intestine,lymph node
Kod klasy składowania
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
“Click” chemistry, and the copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) in particular, is a powerful new synthetic tool in polymer chemistry and material science.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej







![1-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylcarbodiimide methiodide](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/414/134/4eb9c126-d7f9-4e12-9e3a-95cb077824fd/640/4eb9c126-d7f9-4e12-9e3a-95cb077824fd.png)