10786357001
Roche
Rybonukleaza H (RNaza H)
from Escherichia coli H 560 pol A1
Synonim(y):
rnase h
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
Escherichia coli ( H 560 pol A1)
Poziom jakości
Próba
100%
Formularz
solution
aktywność właściwa
~40000 units/mg protein
opakowanie
pkg of 100 U
producent / nazwa handlowa
Roche
metody
cDNA synthesis: suitable
kolor
colorless
optymalne pH
7.5-9.1
rozpuszczalność
water: miscible
przydatność
suitable for molecular biology
numer dostępu NCBI
Zastosowanie
life science and biopharma
obecność zanieczyszczeń
RNase, none detected (up to 10 U with MS- II- RNA)
endonuclease ~10 units, none detected (using lambda-DNA)
nicking activity 10 units, none detected
Warunki transportu
dry ice
temp. przechowywania
−20°C (−15°C to −25°C)
informacje o genach
Escherichia coli ... rnhA(946955)
Opis ogólny
Source: E. coli H560 pol A1
Storage Buffer: 25 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM KCl, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 0.1 mM EDTA, 50% glycerol (v/v), pH 8.0 (+4°C)
Volume Activity: 1 x 103 U/ml assayed according to Hillenbrand & Staudenbauer.
Zastosowanie
- In vivo RNA-primed initiation of DNA synthesis
- Elimination of mRNA during second-strand cDNA synthesis
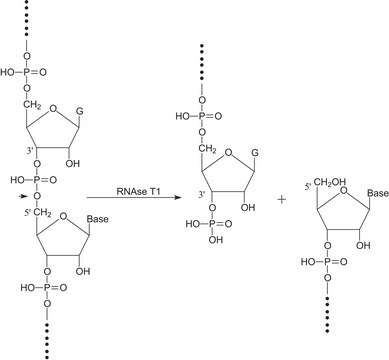
- Site-specific cleavage of RNA
- Detection of RNA:DNA regions in double-stranded DNA of natural origin
- Removal of poly (A) sequences of mRNA if oligo (dT) is present
- RNA extraction and quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Cechy i korzyści
- Eliminate potential sources of PCR errors.
- Increase accessibility of primers during subsequent PCR.
Jakość
Definicja jednostki
Volume Activity: Approximately 1 U/μl
Uwaga dotycząca przygotowania
Przechowywanie i stabilność
Inne uwagi
Kod klasy składowania
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
does not flash
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
does not flash
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej