Key Documents
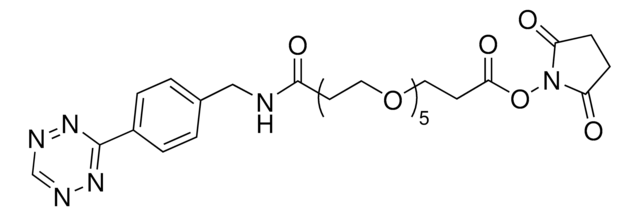
911798
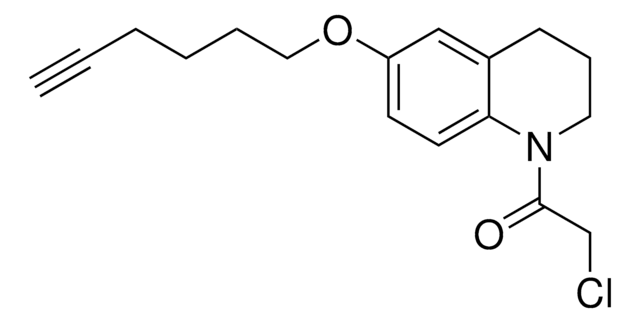
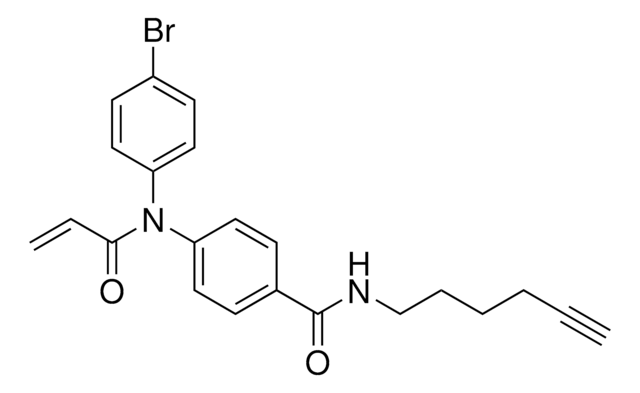
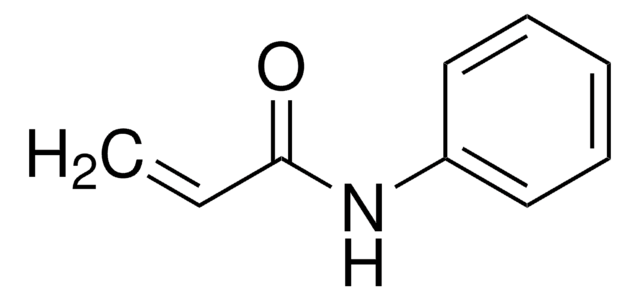
N-(4-Bromophenyl)-N-phenylacrylamide
≥95%
Synonim(y):
Electrophilic scout fragment, KB05, Scout fragment for targetable cysteine
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Zastosowanie
Inne uwagi
Informacje prawne
produkt powiązany
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Przepraszamy, ale COA dla tego produktu nie jest aktualnie dostępny online.
Proszę o kontakt, jeśli potrzebna jest pomoc Obsługa Klienta
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Produkty
Ligandability describes the propensity of a protein target to bind a small molecule with high affinity. It is a precursor to evaluating druggability, which requires more advanced translational pharmacological effects and drug-like properties in vivo.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej