おすすめの製品
形状
lyophilized (white powder to sticky mass to hard pellet)
品質水準
比活性
≥9 units/μg protein (cyclic-AMP is not required for this activity)
分子量
40,862 Da
保管温度
−20°C
詳細
プロテインキナーゼA酵素は、触媒サブユニットおよび調節サブユニットの2つで構成されています。触媒サブユニットは、cAMPの存在下でモノマーとして存在し、分子量は40,862 Daです。
アプリケーション
ウシ心臓由来プロテインキナーゼA(PKA)触媒サブユニットは以下の用途に使用されています
- PKAを介したIRK1(内向き整流K+)チャネルの阻害の研究
- in Vitro PKAリン酸化アッセイ
- in Vitro アフィニティ結合アッセイ
- 機能的に活性を有する運動ニューロンの吸気駆動電流に対するPKAの効果の研究
生物化学的/生理学的作用
プロテインキナーゼAは、ATPから様々なタンパク質に存在するトレオニンまたはセリン残基への末端リン酸の移動を触媒します。このタンパク質は、触媒サブユニットと調節サブユニットが結合しているcAMPの非存在下では不活性です。調節サブユニットは、cAMPの存在下でcAMPに結合し、触媒サブユニットを放出します。
プロテインキナーゼA(PKA)は、ヘッジホッグシグナル伝達を制御し、細胞の増殖および運命特定に関与します。いくつかの神経伝達物質受容体、転写因子およびさまざまな細胞内シグナル伝達経路の構成要素をリン酸化します。
包装
容量は、リン酸化unitを基準にしています。
単位の定義
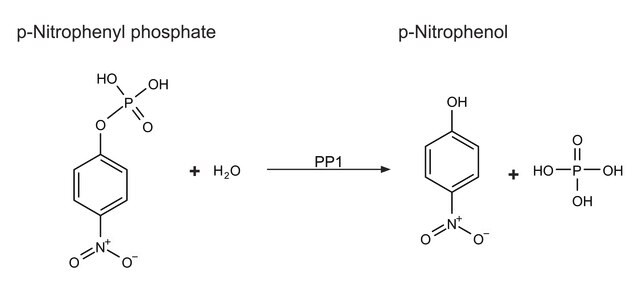
1単位は、pH 6.5、30°Cで1分間に1.0 pmolのリン酸をATPから、加水分解され一部脱リン酸化されたカゼインに転移させる量です(ADPの産生量を測定することにより決定)。
物理的形状
凍結乾燥粉末(安定化剤としてショ糖およびリン酸バッファー塩を含有)。
調製ノート
プロテインキナ-ゼA (P5511)から調製しています。
免責事項
Please note that the pack size has been changed to align with the unit definition, while the number of phosphorylating units remain the same as before.
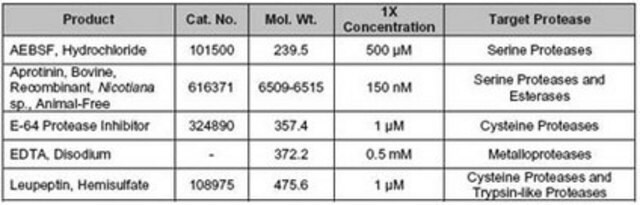
阻害剤
製品番号
詳細
価格
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
P2645-1000UN-PW:
P2645-12.5KU:
P2645-500UN:
P2645-1000UN:
P2645-400UN:
P2645-PH:
P2645-400UN-PW:
P2645-2.5KU:
P2645-1KU:
P2645-BULK:
P2645-100UN:
P2645-250UN:
P2645-VAR:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Cyclic nucleotides in the nervous system
Basic Neurochemistry, 423-441 (2012)
F T Hartl et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 258(6), 3950-3955 (1983-03-25)
The physical and chemical properties of purified catalytic and regulatory subunits of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine brain, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle were compared. The catalytic subunits from all three sources were identical with respect to molecular
Ken Tougane et al.
Plant physiology, 152(3), 1529-1543 (2010-01-26)
Abscisic acid (ABA) is postulated to be a ubiquitous hormone that plays a central role in seed development and responses to environmental stresses of vascular plants. However, in liverworts (Marchantiophyta), which represent the oldest extant lineage of land plants, the
Christopher M Bocchiaro et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 23(4), 1099-1103 (2003-02-25)
Plasticity underlying adaptive, long-term changes in breathing behavior is hypothesized to be attributable to the modulation of respiratory motoneurons by intracellular second-messenger cascades. In quiescent preparations, protein kinases, including cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), potentiate glutamatergic inputs. However, the dynamic
E Wischmeyer et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 93(12), 5819-5823 (1996-06-11)
Strongly rectifying IRK-type inwardly rectifying K+ channels are involved in the control of neuronal excitability in the mammalian brain. Whole-cell patch-clamp experiments show that cloned rat IRK1 (Kir 2.1) channels, when heterologously expressed in mammalian COS-7 cells, are inhibited following
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)