おすすめの製品
由来生物
goat
結合体
unconjugated
抗体製品の状態
affinity isolated antibody
抗体製品タイプ
secondary antibodies
クローン
polyclonal
濃度
2.0 mg/mL
テクニック
Ouchterlony double diffusion: suitable
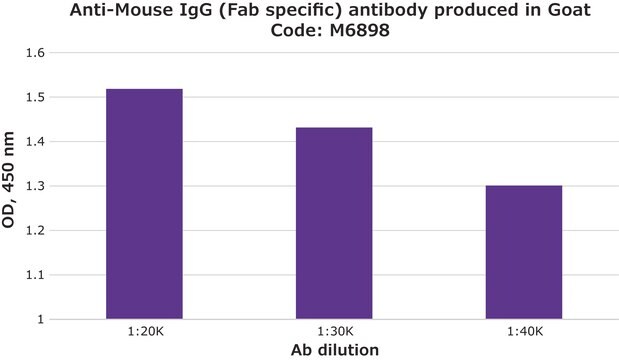
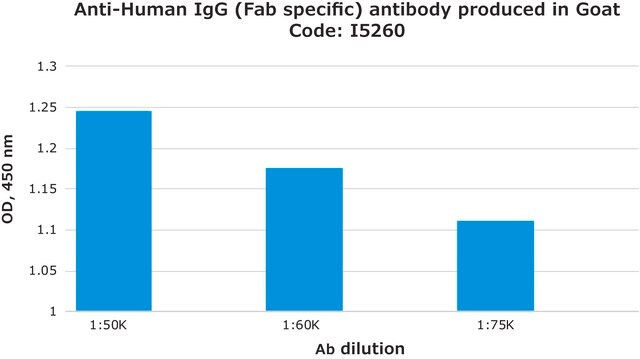
indirect ELISA: 1:15,000
輸送温度
dry ice
保管温度
−20°C
ターゲットの翻訳後修飾
unmodified
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
詳細
IgGは4つのポリペプチド鎖を含み、2つの同一の50 kDa γ重鎖(H)と2つの同一の25 kDa κまたはλ軽鎖(L)で構成されています。これらの鎖は鎖間ジスルフィド結合で接続されています。IgGには、IgG1、IgG2、IgG3、およびIgG4の4種のアイソタイプがあります。
アプリケーション
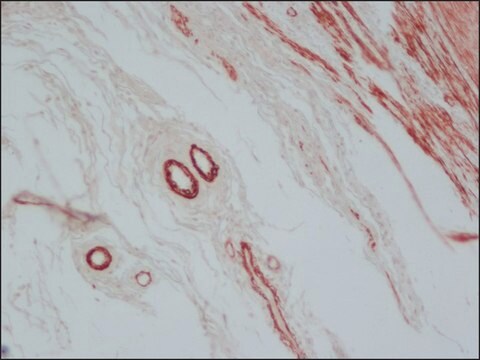
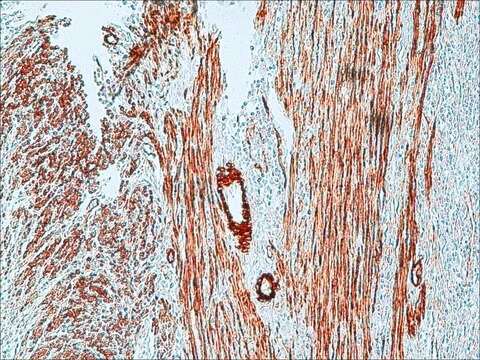
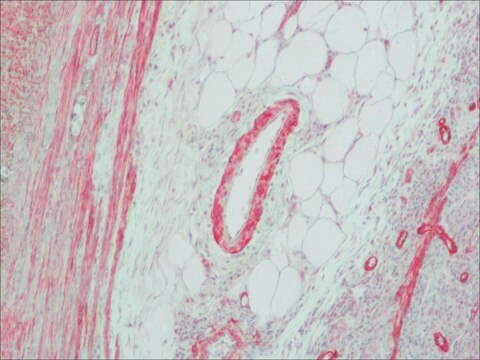
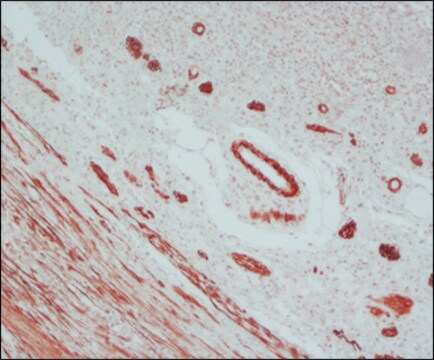
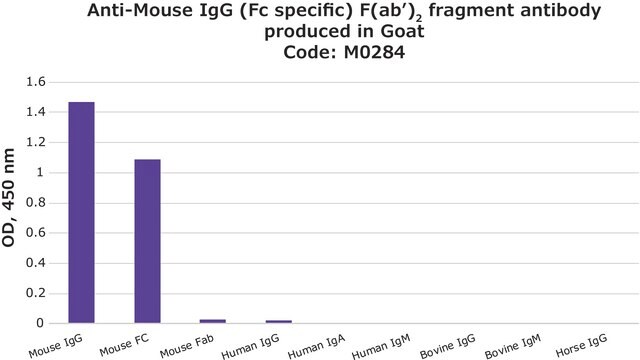
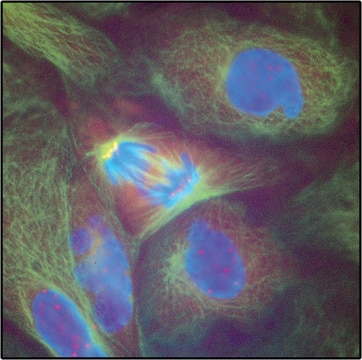
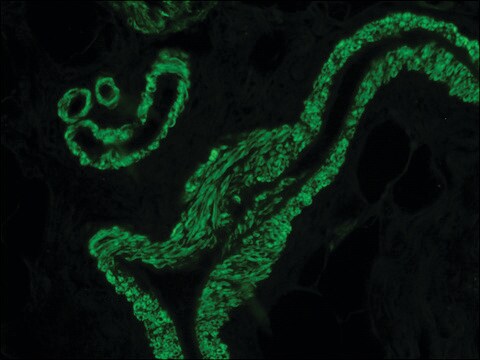
ヤギで産生した抗マウスIgG(Fab特異的)抗体は、1:10の希釈率で免疫細胞化学的染色の二次抗体として使用されました。
ヤギで産生した抗マウスIgG(Fab特異的)抗体は、ヒト血小板第4因子(PF4)および抗PF4モノクローナル抗体の発現および精製で使用されています。
生物化学的/生理学的作用
IgGは補体系の古典的経路を活性化します。ウイルス粒子および毒素を中和します。IgGは、抗体依存性細胞細胞傷害(ADCC)において不可欠な役割を果たします。最も長い血清半減期を持ち、アレルギーと関連している可能性があります。
IgG抗体サブタイプは、免疫系の血清免疫グロブリンの中で最も豊富に存在します。B細胞より分泌され、血液や細胞外液に認められます。また、細菌、真菌およびウイルスが引き起こす感染を防御します。母親のIgGは、胎盤を通して胎児に受け継がれますが、これは、新生児の感染症に対する免疫防御にとって不可欠です。
その他情報
ウシ、ウマおよびヒト血清タンパク質と共に吸着される抗体。
物理的形状
pH 7.4の0.01 Mリン酸緩衝生理食塩水中に15 mMのアジ化ナトリウムを含有する溶液。
免責事項
弊社のカタログまたは製品に添付された弊社のその他の文書に記載されていない場合、弊社の製品は研究用途向けのみを目的としているため、他のいかなる目的にも使用することはできません。このような目的としては、未承認の販売用途、in vitroの診断用途、ex vivoあるいはin vivoの治療用途、またはヒトあるいは動物へのあらゆる種類の消費あるいは適用などがありますが、これらに限定されません。
Not finding the right product?
Try our 製品選択ツール.
保管分類コード
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
M4155-BULK:
M4155-VAR:
M4155-1ML:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
S Peller et al.
Genes, chromosomes & cancer, 21(1), 2-7 (1998-01-27)
The TP53 gene has been extensively studied in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), both in chronic phase and in blast crisis. Mutations in the gene were found in up to 30% of the patients, especially among those in blast
Distinct Specificity and Single-molecule Kinetics of the Interaction of Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic anti-Platelet Factor 4/Heparin Antibodies with Platelet Factor 4
Litvinov RI, et al.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, jbc-M113 (2013)
Joong Ho Shin et al.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 66(1), 290-297 (2017-12-05)
This paper presents a handheld device that is capable of simplifying multistep assays to perform sensitive detection of foodborne pathogens. The device is capable of multiplexed detection of Escherichia coli (E. coli) O157:H7, Salmonella Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium), Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus
Zheng Cai et al.
Nature communications, 6, 8277-8277 (2015-09-24)
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is an autoimmune thrombotic disorder caused by immune complexes containing platelet factor 4 (PF4), antibodies to PF4 and heparin or cellular glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Here we solve the crystal structures of the: (1) PF4 tetramer/fondaparinux complex, (2) PF4
Rustem I Litvinov et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 288(46), 33060-33070 (2013-10-08)
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a thrombotic complication of heparin therapy mediated by antibodies to complexes between platelet factor 4 (PF4) and heparin or cellular glycosaminoglycans. However, only a fraction of patients with anti-PF4-heparin antibodies develop HIT, implying that only a
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)