776130
3-Azido-1-propanol
≥96%
Sinônimo(s):
1-Azidopropan-3-ol
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (Notação de Hill):
C3H7N3O
Número CAS:
Peso molecular:
101.11
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352125
ID de substância PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
≥96%
Formulário
liquid
adequação da reação
reaction type: click chemistry
índice de refração
n20/D 1.461
densidade
1.095 g/mL at 25 °C
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
OCCCN=[N+]=[N-]
InChI
1S/C3H7N3O/c4-6-5-2-1-3-7/h7H,1-3H2
chave InChI
WHVSIWLMCCGHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
3-Azido-1-propanol is an azide-containing reagent utilized in Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition reactions (SPAAC). This enables selective and copper-free click chemistry modifications of biomolecules.
Aplicação
3-Azido-1-propanol is used as a:
- Precursor in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds like dihydrooxazines
- Reagent in the synthesis of heterofunctional polyesters by 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
1, 3-Dipolar and Diels-Alder cycloaddition reactions on polyester backbones possessing internal electron-deficient alkyne moieties
M Cetin, et.al.
Polym. Chem., 7, 7094-7100 (2016)
Efficient synthesis of linear multifunctional poly (ethylene glycol) by copper (I)-catalyzed Huisgen 1, 3-dipolar cycloaddition
Liu X-M, et al.
Biomacromolecules, 8(9), 2653-2658 (2007)
1, 3-Dipolar and Diels-Alder cycloaddition reactions on polyester backbones possessing internal electron-deficient alkyne moieties
Cetin M, et al.
Polym. Chem., 7(46), 7094-7100 (2016)
Cross-linked polymer-blend gate dielectrics through thermal click chemistry
Li S, et al.
Chemistry?A European Journal, 21(49), 17762-17768 (2015)
Somayeh Khezrian et al.
Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A, 108(11), 2291-2304 (2020-05-05)
Active targeted nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems have gained significant favor because they have the ability to decrease side effects, improve drug bioavailability, and the potency of anticancer treatment. In this study, functional amphiphilic Janus nanoparticles (JNPs), consisting of hydrophilic and
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 776130-1G | 4061826736333 |
| 776130-5G | 4061833332627 |
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica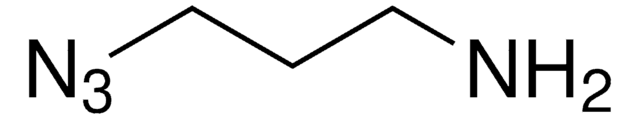
![2-[2-(2-Azidoethoxy)ethoxy]ethanol solution ~0.5 M in tert-butyl methyl ether](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/374/007/eea7ca74-41e4-4aac-af71-c93c37ec0a5a/640/eea7ca74-41e4-4aac-af71-c93c37ec0a5a.png)