OGS589
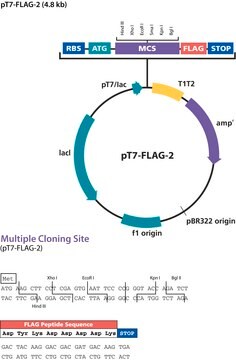
PBR322 - PBR322 LOW COPY CLONING VECTOR
plasmid vector for molecular cloning
Synonym(s):
cloning vector, expression vector, molecular cloning vector, plasmid, plasmid vector, snapfast vector, vector
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
size 4361 bp
bacteria selection
ampicillin
origin of replication
BR322 (15 copies)
peptide cleavage
no cleavage
reporter gene
none
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Promoter Expression Level:
Application
Sequence
Analysis Note
Related product
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Protocols
Sigma-Aldrich presents a technical article to help you choose the right SnapFast™ vector to meet your needs.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service