Kluczowe dokumenty
J2000
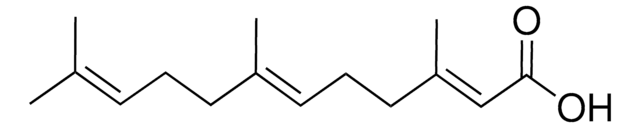
Juvenile hormone III
≥65%, liquid, non-sterile
Synonim(y):
Methyl farnesoate, 10,11-epoxide, C16-Juvenile Hormone, JH-III, Manduca hormone, trans,trans-10,11-Epoxy-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,6-dodecadienic acid methyl ester
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
synthetic (organic)
Poziom jakości
sterylność
non-sterile
Próba
≥65% (HPLC)
Formularz
liquid
stężenie
≥65%
metody
activity assay: suitable
Warunki transportu
ambient
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
ciąg SMILES
COC(=O)\C=C(/C)CC\C=C(/C)CC[C@H]1OC1(C)C
InChI
1S/C16H26O3/c1-12(9-10-14-16(3,4)19-14)7-6-8-13(2)11-15(17)18-5/h7,11,14H,6,8-10H2,1-5H3/b12-7+,13-11+
Klucz InChI
QVJMXSGZTCGLHZ-ZPLWXOMKSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Juvenile hormone III (JH III) is the most prevalent juvenile hormone (JH) found in insects.
Zastosowanie
- study the effect of juvenile hormone on mictic (sexual) female production of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Muller
- study the effect of juvenile hormone on head GB19811 (putative Takeout/juvenile hormone binding protein) mRNA levels in adult honeybees
- study the effect of juvenile hormone on gonadotropic and physiological functions in bumblebee Bombus terrestris
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Inhibitor
produkt powiązany
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Aquatic Chronic 4
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej