Key Documents
906808
Water-soluble TPO based nanoparticle photoinitiator
contains ionic surfactant
Synonim(y):
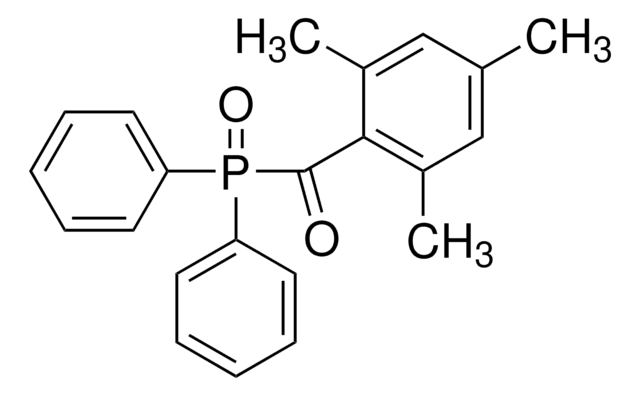
Diphenyl(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide, TPO
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Postać
powder or solid
kolor
white to off-white
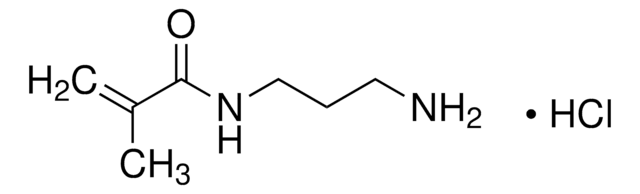
ciąg SMILES
O=P(C1=CC=CC=C1)(C(C2=C(C)C=C(C)C=C2C)=O)C3=CC=CC=C3
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Zastosowanie
The extinction coefficient of the new water-dispersible nanoparticles of TPO is more than 300 times larger than the best and most used commercially available water-soluble photoinitiator, Irgacure 2959. The TPO nanoparticles absorb significantly in the range from 385 to 420 nm, making them suitable for use in commercially available, low-cost, light-emitting diode-based 3D printers and UV-curing devices.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Dam. 1 - Repr. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
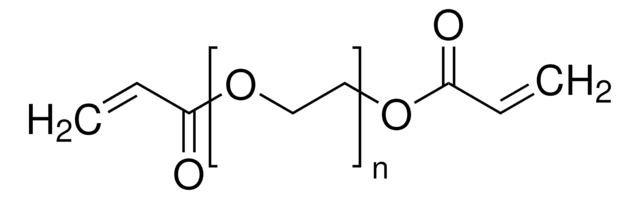
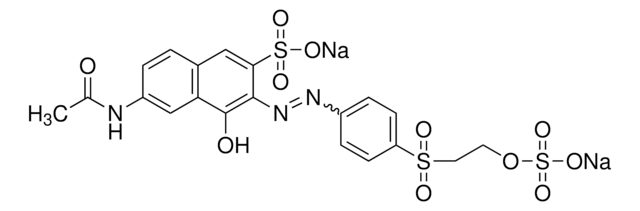
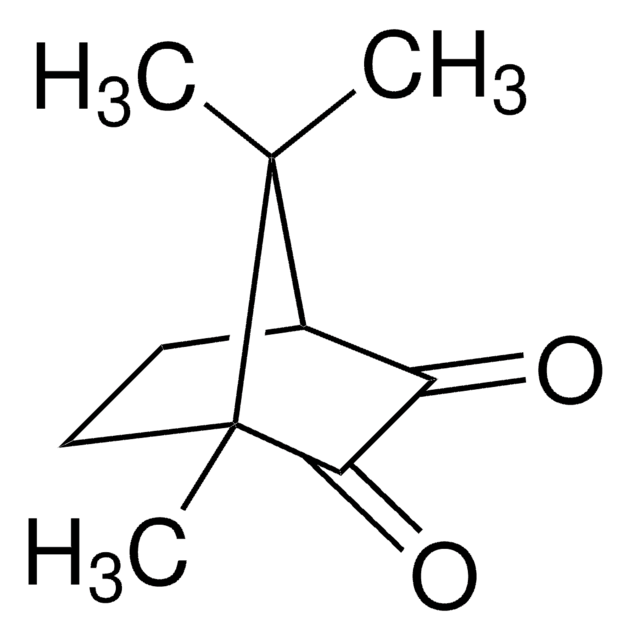
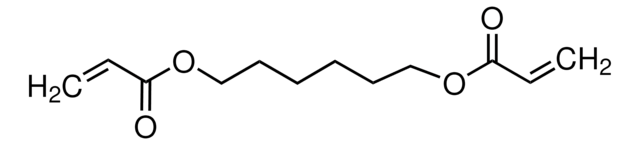
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
The introduction of LAP and water-dispersible photoinitiator nanoparticles of TPO, enables the development of novel formulations for 3D bioprinting, tissue engineering applications, and device manufacturing.
Powiązane treści
Inżynieria tkankowa wytwarza kultury tkanek z rusztowań, żywych komórek i biologicznie aktywnych cząsteczek, symulując mikrośrodowisko organizmu w celu naprawy lub zastąpienia uszkodzonej tkanki.
Tissue engineering fabricates tissues cultures from scaffolds, living cells, and biologically active molecules by simulating the microenvironment of the body to repair or replace damaged tissue.
Inżynieria tkankowa wytwarza kultury tkanek z rusztowań, żywych komórek i biologicznie aktywnych cząsteczek, symulując mikrośrodowisko organizmu w celu naprawy lub zastąpienia uszkodzonej tkanki.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej