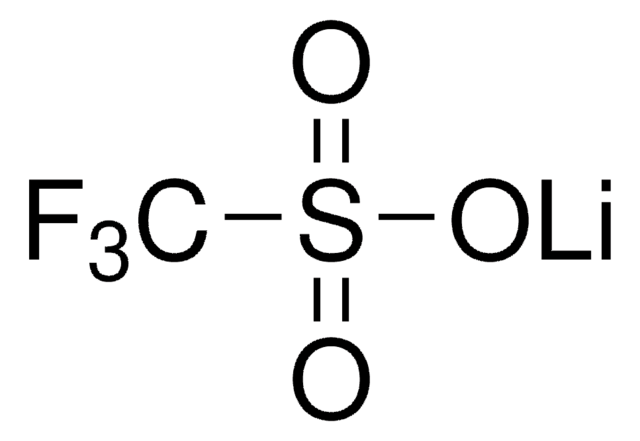
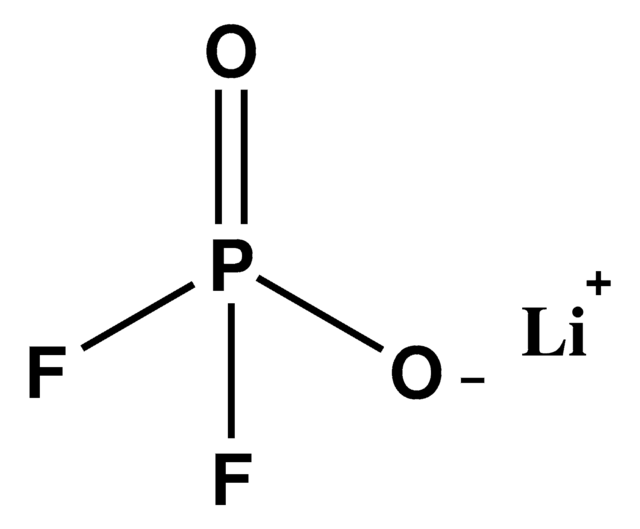
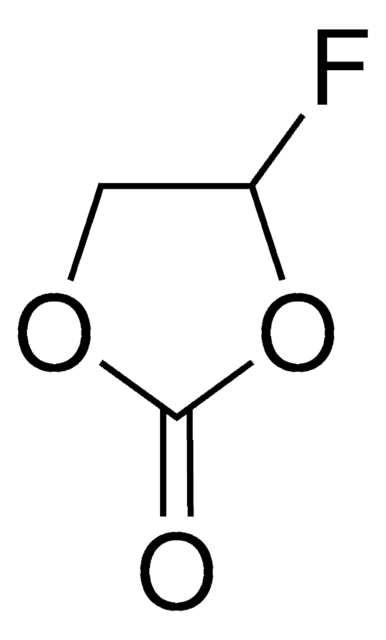
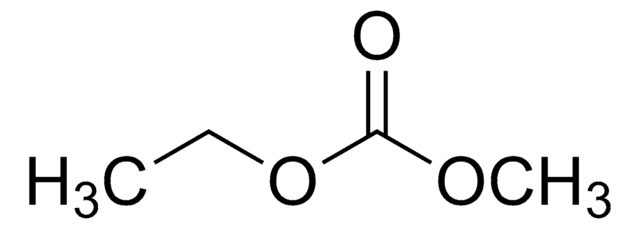
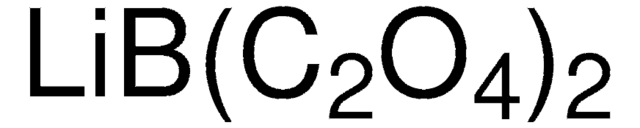Kluczowe dokumenty
774138
Lithium difluoro(oxalato)borate
Synonim(y):
LIDFOB, LIF2OB, LIFOB, LIODFB, Lithium difluoro(ethanedioato)borate, Lithium oxalatodigluoroborate
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Postać
powder
Poziom jakości
charakterystyka ekologicznej alternatywy
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
mp
265-271 °C
Zastosowanie
battery manufacturing
kategoria ekologicznej alternatywy
, Enabling
ciąg SMILES
F[B-]1(OC(C(O1)=O)=O)F.[Li+]
InChI
1S/C2BF2O4.Li/c4-3(5)8-1(6)2(7)9-3;/q-1;+1
Klucz InChI
MEDDCIKGDMDORY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Cechy i korzyści
✔ Increases battery life
✔ Stabilizes SEI layer
✔ Suitable for fast charging and low temperatures
produkt powiązany
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Dr. Sun reviews the recent advances in solid-state rechargeable batteries and cover the fundamentals of solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries, the theory of ion conduction, and the structures and electrochemical processes of solid-state Li batteries.
Półprzewodnikowe akumulatory Li: Przegląd elektrolitów stałych, przewodzenia jonów, struktur i procesów elektrochemicznych.
Li-ion batteries are currently the focus of numerous research efforts with applications designed to reduce carbon-based emissions and improve energy storage capabilities.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely adopted as the most promising portable energy source in electronic devices because of their high working voltage, high energy density, and good cyclic performance.
Powiązane treści
Baterie, ogniwa paliwowe i superkondensatory opierają się na elektrochemicznym wytwarzaniu energii. Zrozumienie ich działania i separacji transportu elektronów/jonów.
Baterie, ogniwa paliwowe i superkondensatory opierają się na elektrochemicznym wytwarzaniu energii. Zrozumienie ich działania i separacji transportu elektronów/jonów.
Batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors rely on electrochemical energy production. Understand their operation and electron/ion transport separation.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej