Wszystkie zdjęcia(3)
Key Documents
683957
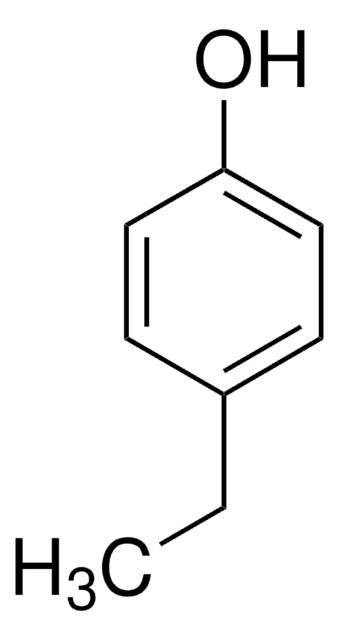
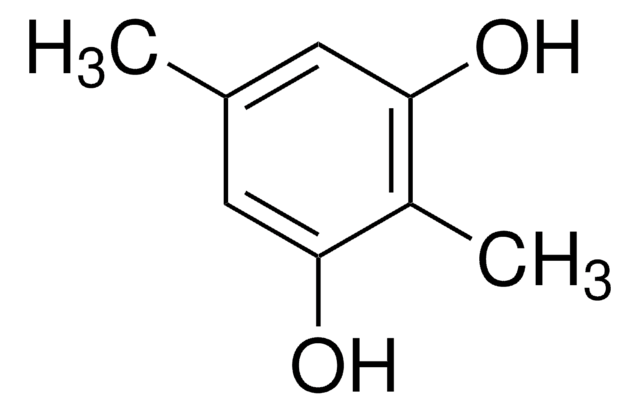
4-Ethylcatechol
95%
Synonim(y):
3,4-Dihydroxyethylbenzene
Zaloguj sięWyświetlanie cen organizacyjnych i kontraktowych
About This Item
Wzór empiryczny (zapis Hilla):
C8H10O2
Numer CAS:
Masa cząsteczkowa:
138.16
Numer WE:
Numer MDL:
Kod UNSPSC:
12352100
Identyfikator substancji w PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Polecane produkty
Próba
95%
Postać
solid
mp
34-45 °C
ciąg SMILES
CCc1ccc(O)c(O)c1
InChI
1S/C8H10O2/c1-2-6-3-4-7(9)8(10)5-6/h3-5,9-10H,2H2,1H3
Klucz InChI
HFLGBNBLMBSXEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Powiązane kategorie
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
>230.0 °F - closed cup
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
> 110 °C - closed cup
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Gautam Gaur et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 86(5) (2019-12-22)
Phenolic acids are among the most abundant phenolic compounds in edible parts of plants. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) metabolize phenolic acids, but the enzyme responsible for reducing hydroxycinnamic acids to phenylpropionic acids (HcrB) was only recently characterized in Lactobacillus plantarum
Robert Brüninghoff et al.
Environmental science & technology, 53(15), 8725-8735 (2019-07-10)
We evaluated electrochemical degradation (ECD) and photocatalytic degradation (PCD) technologies for saline water purification, with a focus on rate comparison and formation and degradation of chlorinated aromatic intermediates using the same non-chlorinated parent compound, 4-ethylphenol (4EP). At 15 mA·cm-2, and
Raffaele Guzzon et al.
Journal of food science and technology, 54(3), 810-821 (2017-03-17)
Careful control of spoilage microflora inside wine containers is a key issue during winemaking. To date, attention has been paid to the development of an effective protocol for the eradication of spoilage agents, especially
Mario Malacarne et al.
Food chemistry, 206, 274-283 (2016-04-05)
Commercial tannins from several botanical sources and with different chemical and technological characteristics are used in the food and winemaking industries. Different ways to check their botanical authenticity have been studied in the last few years, through investigation of different
Nicholas S Kruyer et al.
Scientific reports, 10(1), 13367-13367 (2020-08-10)
Microbial production of adipic acid from lignin-derived monomers, such as catechol, is a greener alternative to the petrochemical-based process. Here, we produced adipic acid from catechol using catechol 1,2-dioxygenase (CatA) and a muconic acid reductase (MAR) in Escherichia coli. As
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej