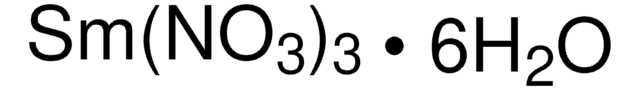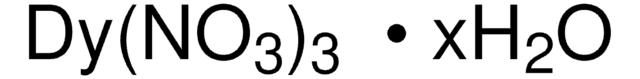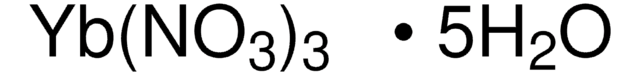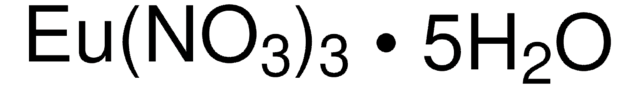Kluczowe dokumenty
205133
Praseodymium(III) nitrate hexahydrate
99.9% trace metals basis
Synonim(y):
Praseodymium trinitrate hexahydrate
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
for analytical purposes
Próba
99.9% trace metals basis
Formularz
crystalline
przydatność reakcji
reagent type: catalyst
core: praseodymium
zanieczyszczenia
≤2000 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
ciąg SMILES
O.O.O.O.O.O.[Pr+3].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/3NO3.6H2O.Pr/c3*2-1(3)4;;;;;;;/h;;;6*1H2;/q3*-1;;;;;;;+3
Klucz InChI
LXXCECZPOWZKLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- A dopant to fabricate dye-sensitized solar cells. The addition of rare earth enhances the power conversion efficiency of solar cells by narrowing the band gap of photoanode materials.
- A precursor to synthesize high entropy lanthanide oxysulfides ( wide band gap semiconductors).
- To synthesize functionalized UV-emitting nanocomposite for photodynamic cancer therapy.
- To fabricate Pr-doped MoO3 thinfilms for gas sensing applications.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Ox. Sol. 3 - Skin Irrit. 2
Kod klasy składowania
5.1B - Oxidizing hazardous materials
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Innovation in dental restorative materials is driven by the need for biocompatible and natural-appearing restoration alternatives. Conventional dental materials like amalgam and composite resins have inherent disadvantages.
The rare earth elements impact nearly everyone in the world. All of the people living in advanced technological countries and almost all those living in third world countries utilize the rare earths in their everyday living—the car that one drives (gasoline is refined from oil using rare earth catalysts and catalytic converters reduce the polluting emissions from the automotive exhaust), watching the news on TV (the red and green colors in TV screens), the telephones and computers we use to communicate (the permanent magnets in speakers and disc drives), just to name a few examples.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej