おすすめの製品
由来生物
bacterial (Flavobacterium heparinum)
品質水準
結合体
conjugate (Glucosaminoglycan)
フォーム
lyophilized powder
比活性
≥200 units/mg protein
濃度
≥200 unit/mg protein (enzyme + BSA)
輸送温度
dry ice
保管温度
−20°C
詳細
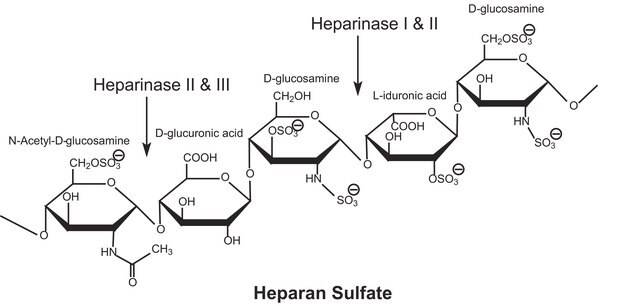
ヘパリナーゼは、細胞外以外のヘパリンを分解する誘導酵素です。3種類のヘパリナーゼがFlavobacterium heparinum (土壌細菌)により産生され、ヘパリンの特異的配列が含まれます。
アプリケーション
Flavobacterium heparinum(土壌細菌)から得られたヘパリナーゼIおよびIII混合物は、以下の用途に使用されています。
- ヒツジ硝子体からのヘパラン硫酸の消化
- ヒト胚腎細胞
- 動脈組織から得られたグリコサミノグリカン
- P0網膜消化
生物化学的/生理学的作用
ヘパリナーゼIおよびIIIは、以下のさまざまな生物学的プロセスにおいて重要な役割を担います:細胞増殖因子相互作用の調整、細胞とリポタンパク質との相互作用、血管新生。 多糖類の2-O-硫酸化 α-L-イドピラノシルウロン酸およびβ-D-グルコピラノシルウロン酸残基の存在下で高度に硫酸化された多糖鎖を切断します。
ヘパリン硫酸プロテオグリカンを主な基質として認識するヘパリン分解リアーゼ。
包装
ヘパリナーゼ1単位当たりで販売。
単位の定義
1単位から、ヘパリナーゼIの基質としてヘパリンナトリウムを使用してpH7.5、25℃において1時間当たり0.1マイクロモルの不飽和ウロン酸が生成します。
1単位から、ヘパリナーゼIIIの基質としてウシ腎臓由来ヘパラン硫酸を使用してpH 7.5、25℃において1時間当たり0.1マイクロモルの不飽和ウロン酸が生成します。
1単位から、pH 7.5、25℃において1時間当たり0.1 μmoleの不飽和ウロン酸が生成します。1国際単位(I.U.)は約600 σ単位と等価です。パッケージサイズはσ単位で販売されます。
1単位から、ヘパリナーゼIIIの基質としてウシ腎臓由来ヘパラン硫酸を使用してpH 7.5、25℃において1時間当たり0.1マイクロモルの不飽和ウロン酸が生成します。
1単位から、pH 7.5、25℃において1時間当たり0.1 μmoleの不飽和ウロン酸が生成します。1国際単位(I.U.)は約600 σ単位と等価です。パッケージサイズはσ単位で販売されます。
その他情報
酵素番号:4.2.2.7 Hep Iおよび4.2.2.8 Hep III
保管分類コード
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
H3917-50UN:
H3917-VAR:
H3917-250UN:
H3917-100UN:
H3917-BULK:
H3917-PH:
H3917-100UN-PW:
H3917-250UN-PW:
H3917-50UN-PW:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
S Ernst et al.
Critical reviews in biochemistry and molecular biology, 30(5), 387-444 (1995-01-01)
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) play an intricate role in the extracellular matrix (ECM), not only as soluble components and polyelectrolytes, but also by specific interactions with growth factors and other transient components of the ECM. Modifications of GAG chains, such as isomerization
Farizeh Aalam et al.
PLoS pathogens, 16(10), e1008968-e1008968 (2020-10-20)
Despite 25 years of research, the basic virology of Kaposi Sarcoma Herpesviruses (KSHV) in B lymphocytes remains poorly understood. This study seeks to fill critical gaps in our understanding by characterizing the B lymphocyte lineage-specific tropism of KSHV. Here, we
P M Galliher et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 41(2), 360-365 (1981-02-01)
Heparinase production by Flavobacterium heparinum in complex protein digest medium, with heparin employed as the inducer, has been studied and improved. The maximum productivity of heparinase has been increased 156-fold over that achieved by previously published methods to 375 U/liter
D A Chappell et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 268(19), 14168-14175 (1993-07-05)
Bovine milk lipoprotein lipase (LPL) induced binding, uptake, and degradation of 125I-labeled normal human triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by cultured mutant fibroblasts lacking LDL receptors. The induction was dose-dependent and occurred whether LPL and 125I-lipoproteins were added to incubation media simultaneously or
Cassandra R Blanchette et al.
PLoS genetics, 13(1), e1006525-e1006525 (2017-01-10)
The regulation of cell migration is essential to animal development and physiology. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans shape the interactions of morphogens and guidance cues with their respective receptors to elicit appropriate cellular responses. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans consist of a protein core
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)