10786357001
Roche
Ribonuclease H (RNase H)
from Escherichia coli H 560 pol A1
Sinonimo/i:
rnase h
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
Escherichia coli ( H 560 pol A1)
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
100%
Forma fisica
solution
Attività specifica
~40000 units/mg protein
Confezionamento
pkg of 100 U
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Roche
tecniche
cDNA synthesis: suitable
Colore
colorless
pH ottimale
7.5-9.1
Solubilità
water: miscible
Compatibilità
suitable for molecular biology
N° accesso NCBI
applicazioni
life science and biopharma
Attività estranea
RNase, none detected (up to 10 U with MS- II- RNA)
endonuclease ~10 units, none detected (using lambda-DNA)
nicking activity 10 units, none detected
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C (−15°C to −25°C)
Informazioni sul gene
Escherichia coli ... rnhA(946955)
Descrizione generale
Source: E. coli H560 pol A1
Storage Buffer: 25 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM KCl, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 0.1 mM EDTA, 50% glycerol (v/v), pH 8.0 (+4°C)
Volume Activity: 1 x 103 U/ml assayed according to Hillenbrand & Staudenbauer.
Applicazioni
- In vivo RNA-primed initiation of DNA synthesis
- Elimination of mRNA during second-strand cDNA synthesis
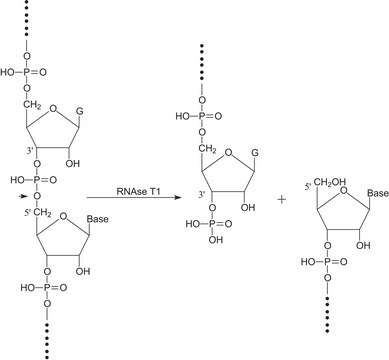
- Site-specific cleavage of RNA
- Detection of RNA:DNA regions in double-stranded DNA of natural origin
- Removal of poly (A) sequences of mRNA if oligo (dT) is present
- RNA extraction and quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
- Eliminate potential sources of PCR errors.
- Increase accessibility of primers during subsequent PCR.
Qualità
Definizione di unità
Volume Activity: Approximately 1 U/μl
Nota sulla preparazione
Stoccaggio e stabilità
Altre note
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
does not flash
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
does not flash
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.