11119915001
Roche
RNase, DNase-free
from bovine pancreas
Sinonimo/i:
Rnase
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
41105600
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
bovine pancreas
Livello qualitativo
Stato
solution
Attività specifica
≥30 units/mg protein
Confezionamento
pkg of 500 μg (1 ml)
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Roche
tecniche
DNA purification: suitable
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Descrizione generale
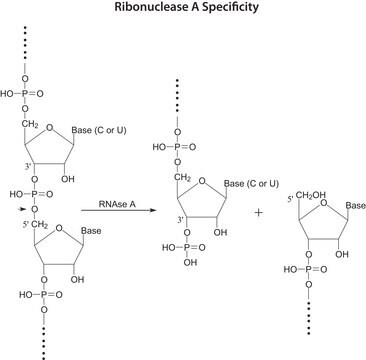
Pyrimidine-specific endoribonuclease that acts on single-stranded RNA. RNase, DNase-free, is a heterogeneous mixture of ribonucleases that has been prepared free of deoxyribonuclease activity according to the current Quality Control procedures. RNase, DNase-free, is particularly well suited for use in DNA isolation procedures. Before use, most RNase preparations must be boiled to remove DNase activity. This preparation of RNase does not need to be boiled; it can be used directly from the vial.
Applicazioni
RNase, DNase-free, efficiently removes contaminating RNA from plasmid or genomic DNA preparations.
Definizione di unità
One Kunitz unit is the amount of enzyme that causes a decrease in absorbance of A0 to A1 within one minute under the assay conditions. A0 to A1 corresponds to the total conversion, A1 being the final absorbance.
One unit produces a decrease in absorbance at 260 nm, which is equivalent to a total conversion of RNA to oligonucleotides in one minute at +25 °C.
One unit produces a decrease in absorbance at 260 nm, which is equivalent to a total conversion of RNA to oligonucleotides in one minute at +25 °C.
Stato fisico
Solution, 500 μg/ml, in 10 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM CaCl2, 50% glycerol (pH 7.0).
Nota sulla preparazione
Working concentration: The optimal working concentration for RNase, DNase free, is 2 to 5 μg/ml. The reaction volume will vary for different applications. Some suggested guidelines are given below:
Working solution: Storage and Dilution Buffer: 10 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM CaCl2, 50% glycerol (v/v), pH 7.0.
- For small-scale isolation of plasmid DNA ("miniprep" from a 1.5 ml bacterial culture), use 0.5 μl of RNase, DNase-free in a reaction volume of 50 μl.
- To isolate plasmid DNA from a 100 ml bacterial culture, use 8 μl of RNase, DNase-free in a reaction volume of 2 ml.
- To isolate genomic DNA from cultured mammalian cells (5 x 107 cells), use 8 μl of RNase, DNase-free in a reaction volume of 2 ml.
Working solution: Storage and Dilution Buffer: 10 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM CaCl2, 50% glycerol (v/v), pH 7.0.
Altre note
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
No data available
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
No data available
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Stacy M Horner et al.
Journal of virology, 81(12), 6254-6264 (2007-03-30)
Viral DNA binding proteins that direct nucleases or other protein domains to viral DNA in lytically or latently infected cells may provide a novel approach to modulate viral gene expression or replication. Cervical carcinogenesis is initiated by high-risk human papillomavirus
Minoo Rassoulzadegan et al.
Cells, 10(6) (2021-07-03)
Local three-stranded DNA/RNA hybrid regions of genomes (R-loops) have been detected either by binding of a monoclonal antibody (DRIP assay) or by enzymatic recognition by RNaseH. Such a structure has been postulated for mouse and human telomeres, clearly suggested by
Jasvinder S Ahuja et al.
Molecular cell, 81(20), 4258-4270 (2021-08-29)
Currently favored models for meiotic recombination posit that both noncrossover and crossover recombination are initiated by DNA double-strand breaks but form by different mechanisms: noncrossovers by synthesis-dependent strand annealing and crossovers by formation and resolution of double Holliday junctions centered
Vasudevan Achuthan et al.
Bio-protocol, 5(12) (2015-06-20)
The PCR- based- α- complementation assay is an effective technique to measure the fidelity of polymerases, especially RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RDRP) and Reverse Transcriptases (RT). It has been successfully employed to determine the fidelity of the poliovirus polymerase 3D-pol (DeStefano
Donna E Akiyoshi et al.
PLoS pathogens, 5(1), e1000261-e1000261 (2009-01-10)
Enterocytozoon bieneusi is the most common microsporidian associated with human disease, particularly in the immunocompromised population. In the setting of HIV infection, it is associated with diarrhea and wasting syndrome. Like all microsporidia, E. bieneusi is an obligate, intracellular parasite
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.