About This Item
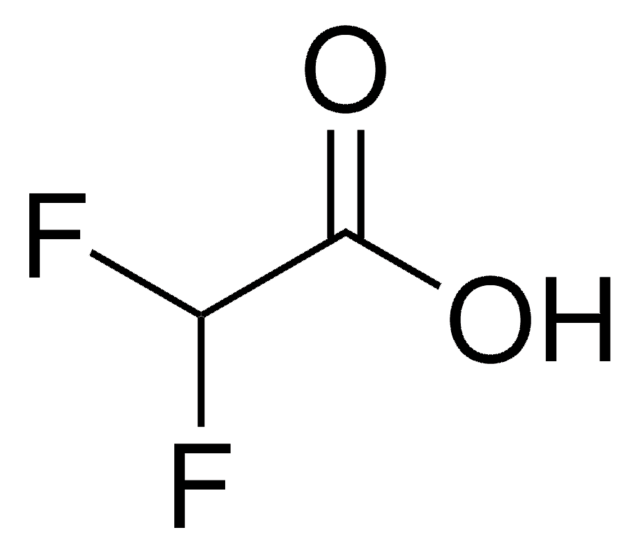
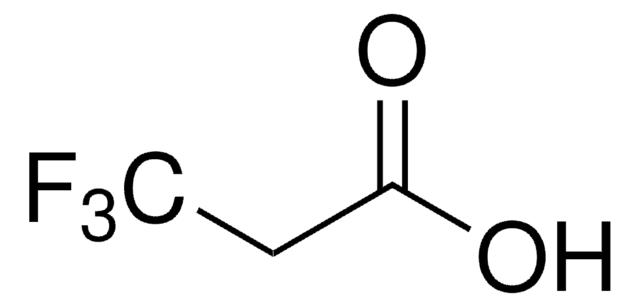
Fórmula linear:
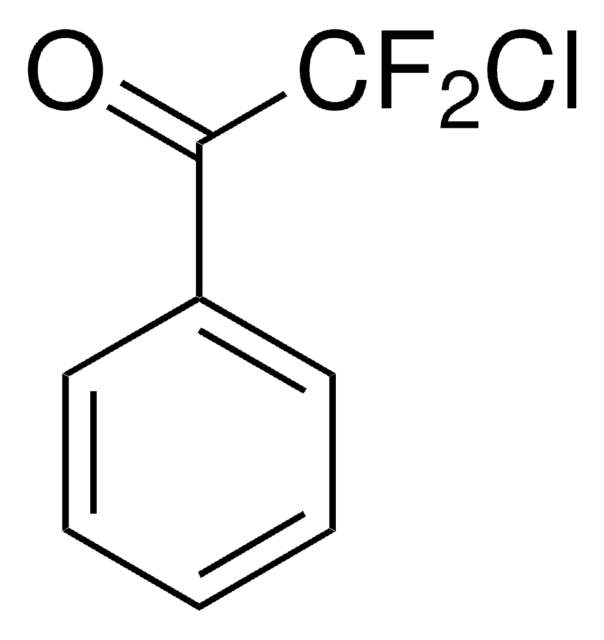
F2ClCCOOH
Número CAS:
Peso molecular:
130.48
Beilstein:
956625
Número CE:
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352106
ID de substância PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Produtos recomendados
Ensaio
98%
Formulário
liquid
índice de refração
n20/D 1.355 (lit.)
p.e.
122 °C (lit.)
pf
20-23 °C (lit.)
densidade
1.54 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
OC(=O)C(F)(F)Cl
InChI
1S/C2HClF2O2/c3-2(4,5)1(6)7/h(H,6,7)
chave InChI
OAWAZQITIZDJRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Skin Corr. 1A
Código de classe de armazenamento
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
J W Harris et al.
Chemical research in toxicology, 4(2), 180-186 (1991-03-01)
1,2-Dichloro-1,1-difluoroethane (HCFC-132b) is a potential substitute for some ozone-depleting chlorofluorocarbons and a model for other 1,1,1,2-tetrahaloethanes under consideration as chlorofluorocarbon substitutes. Male Fischer 344 rats were given 10 mmol/kg HCFC-132b dissolved in corn oil by intraperitoneal injection. An NMR assay
Keith R Solomon et al.
Photochemical & photobiological sciences : Official journal of the European Photochemistry Association and the European Society for Photobiology, 2(1), 62-67 (2003-03-28)
Increased UV-B through stratospheric ozone depletion leads to an increased chemical activity in the lower atmosphere (the troposphere). The effect of stratospheric ozone depletion on tropospheric ozone is small (though significant) compared to the ozone generated anthropogenically in areas already
M L Hanson et al.
Environmental toxicology and chemistry, 20(12), 2758-2767 (2002-01-05)
Chlorodifluoroacetic acid (CDFA) is a novel haloacetic acid (HAA) and has been recently documented in aquatic systems. It is a suspected degradation product of the refrigerants 1,1,2-trichloro-1,1-difluoroethane (CFC-113) and 1-chloro-1,1-difluoroethane (HCFC-142b). Haloacetic acids can be phytotoxic, putatively acting through inhibition
M Zdanowska-Fraczek et al.
Solid state nuclear magnetic resonance, 6(2), 141-146 (1996-04-01)
The reorientation of CClF2 groups in N(CH3)4H(ClF2CCOO)2 has been studied using pulsed NQR and NMR techniques. The temperature dependence of both chlorine (35Cl) NQR and fluorine (19F) NMR spin-lattice relaxation has been measured T1Q of chlorine is attributed to the
Janina Kopyra et al.
The Journal of chemical physics, 135(12), 124307-124307 (2011-10-07)
Negative ion formation following resonant electron attachment to the three title molecules is studied by means of a beam experiment with mass spectrometric detection of the anions. All three molecules exhibit a pronounced resonance in the energy range around 1
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica