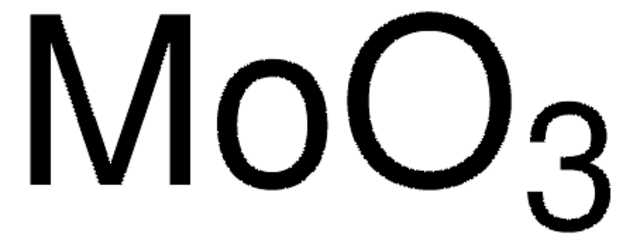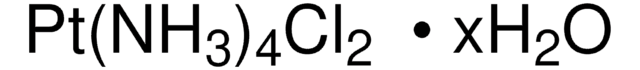Key Documents
M0753
Molybdenum(VI) oxide
ReagentPlus®, ≥99.5%
Synonim(y):
Molybdenum trioxide
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
linia produktu
ReagentPlus®
Próba
≥99.5%
Postać
crystals
przydatność reakcji
reagent type: catalyst
core: molybdenum
mp
795 °C (lit.)
ślady kationów
NH4+: ≤0.02%
ciąg SMILES
O=[Mo](=O)=O
InChI
1S/Mo.3O
Klucz InChI
JKQOBWVOAYFWKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Zastosowanie
Informacje prawne
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Carc. 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej