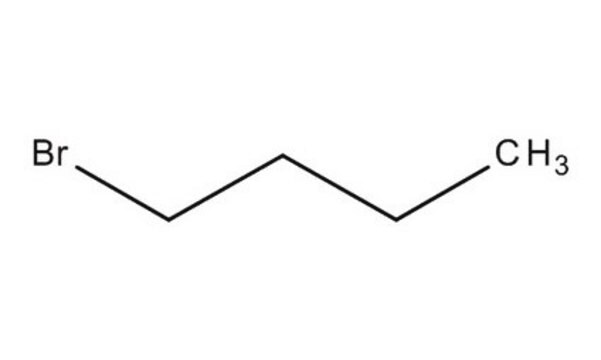
1.01692
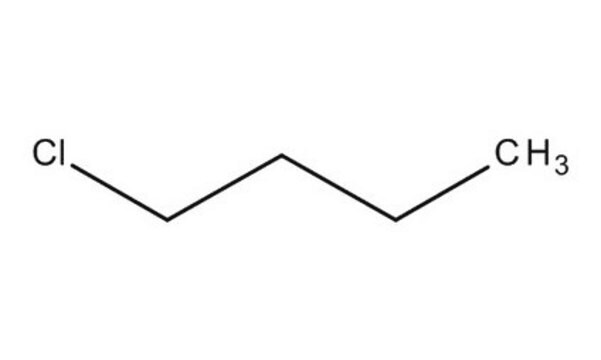
1-Chlorobutane
for liquid chromatography LiChrosolv®
Synonim(y):
1-Chlorobutane, n-Butyl chloride
About This Item
Polecane produkty
ciśnienie pary
110 hPa ( 20 °C)
Poziom jakości
linia produktu
LiChrosolv®
klasa czystości
isocratic
Próba
≥99.8% (GC)
Formularz
liquid
temp. samozapłonu
280 °C
siła działania
2200 mg/kg LD50, oral (Rat)
granice wybuchowości
1.8-10.1 % (v/v)
metody
HPLC: suitable
zanieczyszczenia
≤0.0002 meq/g Acidity
≤0.0002 meq/g Alkalinity
≤0.01% Water
pozostałość po odparowaniu
≤2.0 mg/L
przepuszczalność
227 nm, ≥60%
232 nm, ≥80%
250 nm, ≥98%
bp
79 °C/1013 hPa
mp
-123 °C
temp. przejścia
flash point -17 °C
gęstość
0.886 g/cm3 at 20 °C
temp. przechowywania
2-30°C
InChI
1S/C4H9Cl/c1-2-3-4-5/h2-4H2,1H3
Klucz InChI
VFWCMGCRMGJXDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- Cl atoms-initiated degradation of 1-Chlorobutane and 2-Chlorobutane: This study investigates the kinetics and product analysis of the degradation of 1-Chlorobutane initiated by chlorine atoms. It provides insights into the atmospheric implications of halogenated hydrocarbons, relevant for environmental monitoring and analysis (Kar & Rajakumar, 2023).
- Efficient Remediation of p-chloroaniline Contaminated Soil: Utilizing activated persulfate in the presence of nanosized zero-valent iron/biochar composites, this study demonstrates a method that might be adaptable for the remediation of environments contaminated with similar compounds like 1-Chlorobutane. This is particularly valuable for environmental scientists and lab technicians working on soil decontamination (Guo et al., 2023).
- Rate Coefficient and Mechanism of the OH-Initiated Degradation of 1-Chlorobutane: Focusing on the atmospheric degradation of 1-Chlorobutane by hydroxyl radicals, this research provides critical data for understanding the environmental impact and the chemical behavior of 1-Chlorobutane in the atmosphere, important for researchers in environmental science and atmospheric chemistry (Jara-Toro et al., 2020).
- Genetic programming of catalytic Pseudomonas putida biofilms for boosting biodegradation of haloalkanes: This research demonstrates the genetic modification of bacteria to enhance their ability to degrade haloalkanes, including 1-Chlorobutane. This could interest principle investigators in biotech and pharma researching new methods of biodegradation for industrial applications (Benedetti et al., 2016).
Uwaga dotycząca przygotowania
Komentarz do analizy
Identity (IR): conforms
Evaporation residue: ≤ 2.0 mg/l
Water: ≤ 0.01 %
Acidity: ≤ 0.0002 meq/g
Alkalinity: ≤ 0.0002 meq/g
Transmission (at 227 nm): ≥ 60 %
Transmission (at 232 nm): ≥ 80 %
Transmission (from 250 nm): ≥ 98 %
Filtered by 0.2 µm filter
Inne uwagi
Informacje prawne
Nie możesz znaleźć właściwego produktu?
Wypróbuj nasz Narzędzie selektora produktów.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Asp. Tox. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2
Kod klasy składowania
3 - Flammable liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
10.4 °F - closed cup
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
-12 °C - closed cup
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej