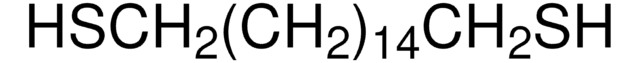Kluczowe dokumenty
705004
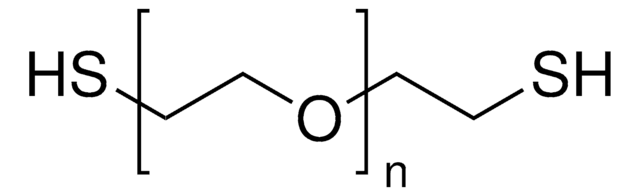
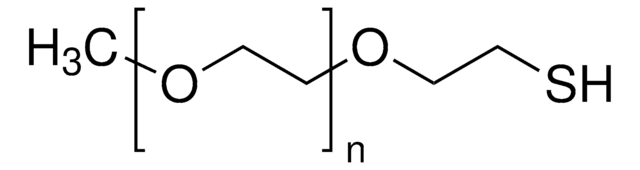
Poly(ethylene glycol) dithiol
average Mn 8,000
Synonim(y):
PEG dithiol ca. 8,000, Poly(ethylene glycol)-dithiol, average Mn 8,000, PEG dithiol
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Postać
powder
masa cząsteczkowa
average Mn 8,000
przydatność reakcji
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reactivity: thiol reactive
mp
63-67 °C
Ω-koniec
thiol
α-koniec
thiol
architektura polimerowa
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Kod klasy składowania
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
nwg
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
The use of hydrogel-based biomaterials for the delivery and recruitment of cells to promote tissue regeneration in the body is of growing interest. This article discussed the application of hydrogels in cell delivery and tissue regeneration.
Omówiono biomateriały na bazie hydrożeli do dostarczania komórek i regeneracji tkanek.
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej