Kluczowe dokumenty
221015
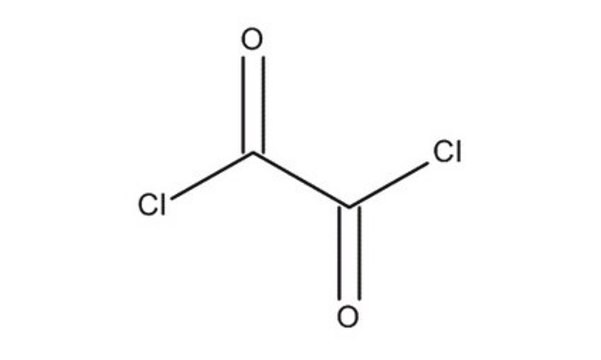
Oxalyl chloride
ReagentPlus®, ≥99%
Synonim(y):
Ethanedioyl dichloride
About This Item
Polecane produkty
gęstość pary
4.4 (vs air)
Poziom jakości
ciśnienie pary
150 mmHg ( 20 °C)
linia produktu
ReagentPlus®
Próba
≥99%
Formularz
liquid
przydatność reakcji
reagent type: oxidant
zanieczyszczenia
<10 ppb Heavy metals
kolor
APHA: 0-150
współczynnik refrakcji
n20/D 1.429 (lit.)
bp
62-65 °C (lit.)
mp
−10-−8 °C (lit.)
gęstość
1.5 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
grupa funkcyjna
acyl chloride
ciąg SMILES
ClC(=O)C(Cl)=O
InChI
1S/C2Cl2O2/c3-1(5)2(4)6
Klucz InChI
CTSLXHKWHWQRSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- Preparation of Mosher′s acid chloride by reacting with Mosher′s acid in the presence of DMF.
- Activation of dimethyl sulfoxide for use in the oxidation of long-chain alcohols to carbonyls.
- Activation of α-keto carboxylic acids and N-heterocyclic carboxylic acids for alkynylation to form ynediones and N-heterocyclic ynones, respectively.
- Synthesis of N-heterocyclic ynones and ynediones, used to activate carboxylic acids
- Chlorination and halogenation
- Three-component [3+2] cycloadditions
- Reactions with organostannanes
- Synthesis of cyclopentenones
- Carbonylations, used as a carbonyl synthon
Opakowanie
Informacje prawne
wyposażenie dodatkowe
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Corr. 1B - Water-react 1
Zagrożenia dodatkowe
Kod klasy składowania
4.3 - Hazardous materials which set free flammable gases upon contact with water
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
51.8 °F - closed cup
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
11.0 °C - closed cup
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej