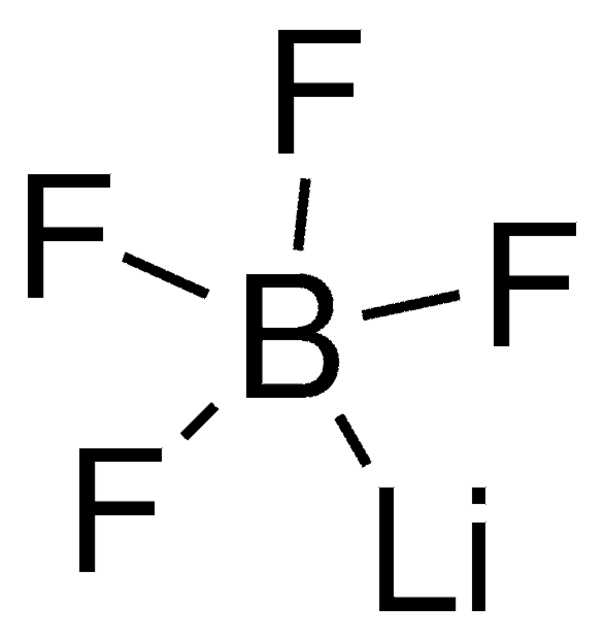
Key Documents
201146
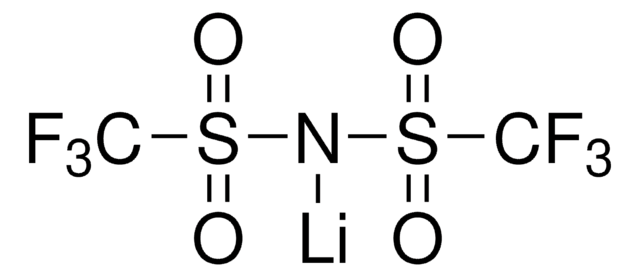
Lithium hexafluorophosphate
98%
Synonim(y):
Lithium phosphorus fluoride
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
Próba
98%
Postać
powder
mp
200 °C (dec.) (lit.)
rozpuszczalność
H2O: slightly soluble(lit.)
gęstość
1.5 g/mL (lit.)
ciąg SMILES
[Li+].F[P-](F)(F)(F)(F)F
InChI
1S/F6P.Li/c1-7(2,3,4,5)6;/q-1;+1
Klucz InChI
AXPLOJNSKRXQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Cechy i korzyści
- It can form suitable SEI membranes in electrodes, especially in the cathode
- It can implement passivation for anode current collectors to prevent their dissolution
- Wide windows of electrical stability
- Excellent solubility and high conductivity in various solvents
- Environment-friendly
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1A - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Organy docelowe
Bone,Teeth
Kod klasy składowania
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
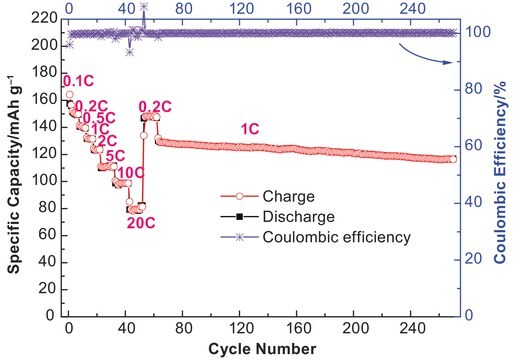
Research and development of solid-state lithium fast-ion conductors is crucial because they can be potentially used as solid electrolytes in all-solid-state batteries, which may solve the safety and energy-density related issues of conventional lithium-ion batteries that use liquid (farmable organic) electrolytes.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej