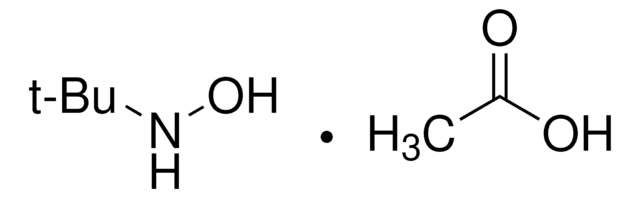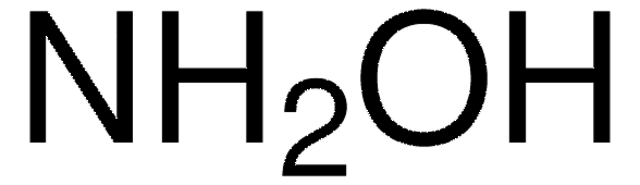Wszystkie zdjęcia(1)
Kluczowe dokumenty
194751
N-tert-Butylhydroxylamine hydrochloride
≥98%
Zaloguj sięWyświetlanie cen organizacyjnych i kontraktowych
About This Item
Wzór liniowy:
(CH3)3CNHOH · HCl
Numer CAS:
Masa cząsteczkowa:
125.60
Beilstein:
3546053
Numer WE:
Numer MDL:
Kod UNSPSC:
12352100
Identyfikator substancji w PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Polecane produkty
Próba
≥98%
Postać
solid
mp
183-185 °C (lit.)
ciąg SMILES
Cl.CC(C)(C)NO
InChI
1S/C4H11NO.ClH/c1-4(2,3)5-6;/h5-6H,1-3H3;1H
Klucz InChI
DCSATTBHEMKGIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Zastosowanie
N-tert-Butylhydroxylamine hydrochloride was used in spin trapping of short-lived radicals. It was also used in the synthesis of α-ketoamides and 3-spirocyclopropanated 2-azetidinones.
Ta strona może zawierać tekst przetłumaczony maszynowo.
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Yu-Kyung Kim et al.
Clinical hemorheology and microcirculation, 40(4), 315-324 (2009-01-08)
Irradiation has been shown to induce biochemical changes in stored red blood cells (RBCs) and to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). This study evaluated the hemorheological properties, the degree of lipid peroxidation and the oxidative susceptibility of irradiated RBCs. Furthermore
Hyun Jeong Kim et al.
Redox report : communications in free radical research, 10(6), 287-293 (2006-01-28)
Heat shock may increase oxidative stress due to increased production of reactive oxygen species and/or the promotion of cellular oxidation events. Therefore, compounds that scavenge reactive oxygen species may regulate heat shock-induced cell death. Recently, it has been shown that
Jin Hyup Lee et al.
Carcinogenesis, 25(8), 1435-1442 (2004-03-16)
Exposure of cells to ionizing radiation leads to formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are associated with radiation-induced cytotoxicity. Therefore, compounds that scavenge ROS may confer radioprotective effects. Recently, it has been shown that the decomposition product of the
David W Killilea et al.
Antioxidants & redox signaling, 5(5), 507-516 (2003-10-29)
Iron accumulates as a function of age in several tissues in vivo and is associated with the pathology of numerous age-related diseases. The molecular basis of this change may be due to a loss of iron homeostasis at the cellular
On the anti-aging activities of aminoguanidine and N-t-butylhydroxylamine.
A R Hipkiss
Mechanisms of ageing and development, 122(2), 169-171 (2001-02-13)
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej