Key Documents
11590
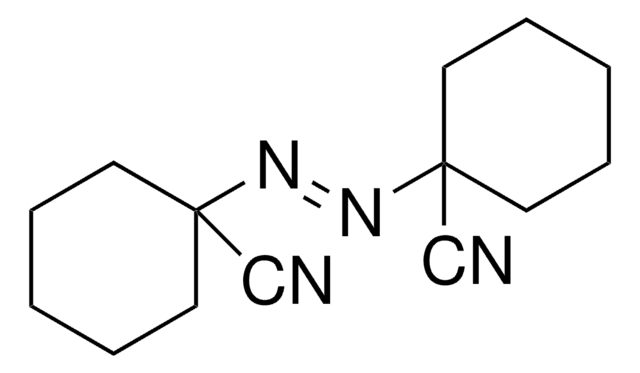
4,4′-Azobis(4-cyanovaleric acid)
≥98.0% (T)
Synonim(y):
4,4′-Azobis(4-cyanopentanoic acid), ABCVA, ACVA
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥98.0% (T)
Postać
solid
zanieczyszczenia
≤1% water
mp
118-125 °C (dec.) (lit.)
grupa funkcyjna
azo
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
ciąg SMILES
CC(CCC(O)=O)(\N=N\C(C)(CCC(O)=O)C#N)C#N
InChI
1S/C12H16N4O4/c1-11(7-13,5-3-9(17)18)15-16-12(2,8-14)6-4-10(19)20/h3-6H2,1-2H3,(H,17,18)(H,19,20)/b16-15+
Klucz InChI
VFXXTYGQYWRHJP-FOCLMDBBSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Zastosowanie
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Self-react. D
Kod klasy składowania
5.2 - Organic peroxides and self-reacting hazardous materials
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
We presents an article regarding common FAQ's for initiators and stabalizers
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Tools for Performing ATRP
We presents an article about Copper(I)-mediated Living Radical Polymerization in the Presence of Pyridylmethanimine Ligands, and the emergence of living radical polymerization mediated by transition metal catalysts in 1995, which was a seminal piece of work in the field of synthetic polymer chemistry.
Protokoły
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
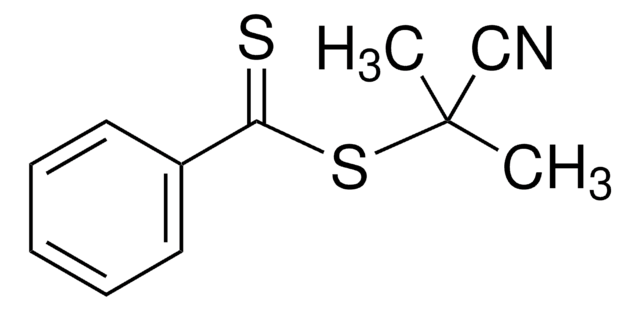
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
Polimeryzacja za pomocą procedur ATRP zademonstrowana przez grupę badawczą prof. Dave'a Haddletona z University of Warwick.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej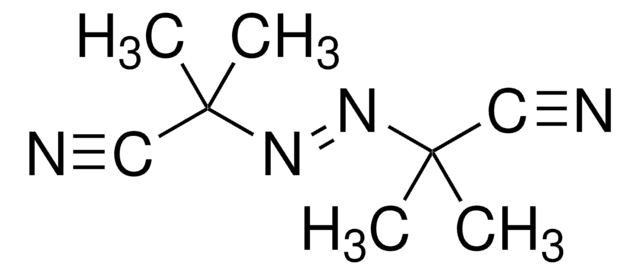
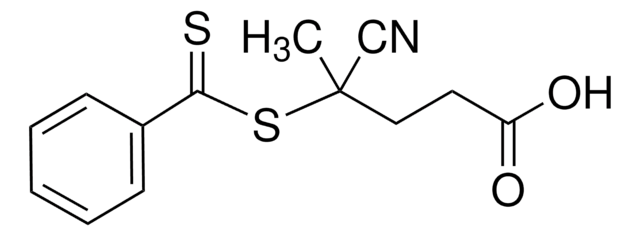
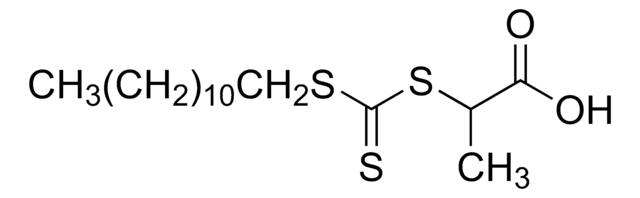
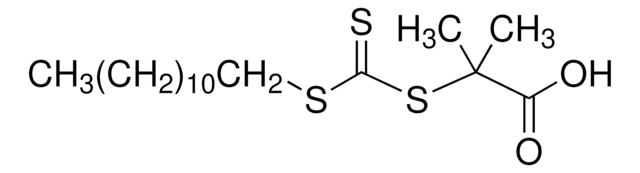
![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)
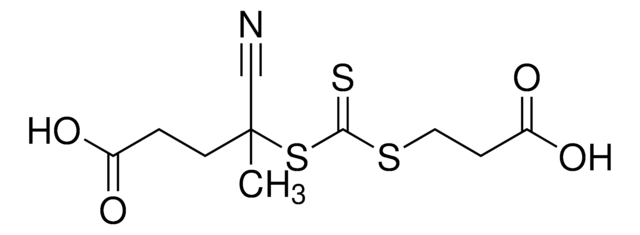
![2-[[(2-Carboxyethyl)sulfanylthiocarbonyl]-sulfanyl]propanoic acid](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/427/606/b02310e2-102e-4324-b09d-e4c0de4fab2c/640/b02310e2-102e-4324-b09d-e4c0de4fab2c.png)