SAE0091
Lisostafina
free of DNA contaminants, ≥500 units/mg protein, lyophilized powder, suitable for Microbiome research
Sinonimo/i:
Glicilglicina endopeptidasi
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
product name
Lisostafina, free of DNA contaminants, suitable for Microbiome research, lyophilized powder, ≥500 units/mg protein
Origine biologica
microbial (Staphylococcus staphylotyticus)
Forma fisica
lyophilized powder
Attività specifica
≥500 units/mg protein
PM
27 kDa
Caratteristiche
DNA free
Condizioni di spedizione
wet ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Applicazioni
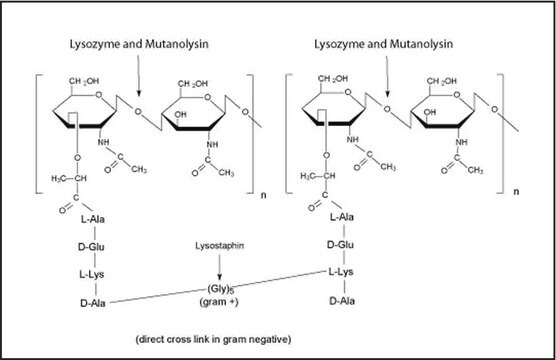
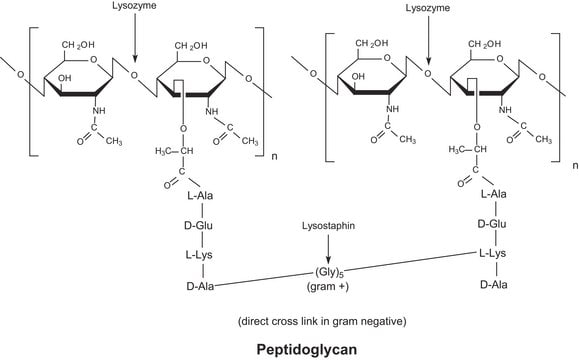
Lysostaphin is a zinc metalloenzyme isolated from a bacterial culture of Staphylococcus staphylolyticus. It has specific lytic action against other Staphylococcus species, including S. aureus.1,2 Lysostaphin has
hexosaminidase, amidase, and endopeptidase activities. It cleaves polyglycine crosslinks in the cellular wall which leads to cell lysis of Staphylococcus species, but not of other bacterial genera. [Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3(4), 1139-1161]
Lysostaphin is a single polypeptide chain of 246 amino acids, a molecular mass of 26,926 Da, isoelectric point of 9.5, (5) and an activity pH optimum of 7.5.(6)
Azioni biochim/fisiol
pH ottimale per l′attività: circa 7,5
Definizione di unità
Stato fisico
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Resp. Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
An overview of human microbiome research, workflow challenges, sequencing, library production, data analysis, and available microbiome reagents to support your research.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.