C6137
Chitinase from Streptomyces griseus
lyophilized powder (essentially salt free), ≥200 units/g solid
Sinonimo/i:
N-acetyl-glucosaminidasechitobiase, Chitin digestion enzymes, poly(β-(1→4)-[2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucoside])- glycanohydrolase
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Forma fisica
lyophilized powder (essentially salt free)
Livello qualitativo
Attività specifica
≥200 units/g solid
PM
30 kDa
Solubilità
H2O: soluble 0.90-1.10 mg/mL
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
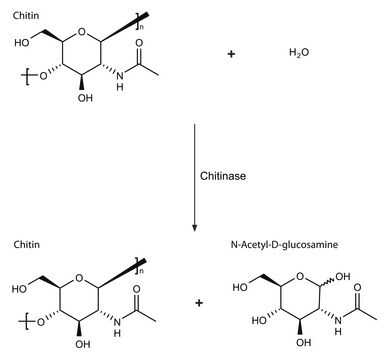
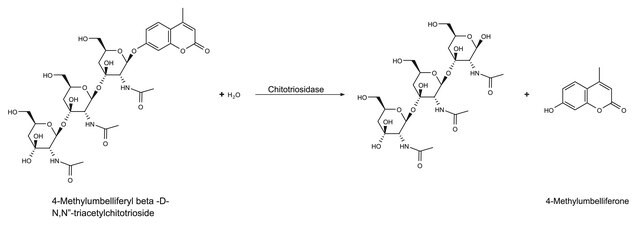
The enzymatic hydrolysis of chitin to N-acetyl-D-glucosamine involves two consecutive enzyme reactions:
- The first reaction, chitodextrinase-chitinase, is a poly(β-(1→4)-[2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucoside])- glycanohydrolase, which removes chitobiose units from chitin.
- The second activity is N-acetyl-glucosaminidasechitobiase, which cleaves the disaccharide to its monomer subunits, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine.
Applicazioni
Human health care: Asthma.
Pharma: preparation of chitooligosaccharides and N-acetyl D glucosamine,
Preparation of single-cell protein
Isolation of protoplasts from fungi and yeast
Control of pathogenic fungi
Treatment of chitinous waste, mosquito control and morphogenesis
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
Definizione di unità
One new 1 hour unit = approx. 50 old 48 hour units.
Substrato
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Resp. Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Contenuto correlato
An overview of cell lysis and protein extraction methods including detergent solubilization, freeze-thaw lysis, osmotic shock, sonication, enzymatic cell lysis, and mechanical disruption techniques such as Dounce, Polytron, and mortar and pestle homogenization.
An overview of cell lysis and protein extraction methods including detergent solubilization, freeze-thaw lysis, osmotic shock, sonication, enzymatic cell lysis, and mechanical disruption techniques such as Dounce, Polytron, and mortar and pestle homogenization.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.