419699
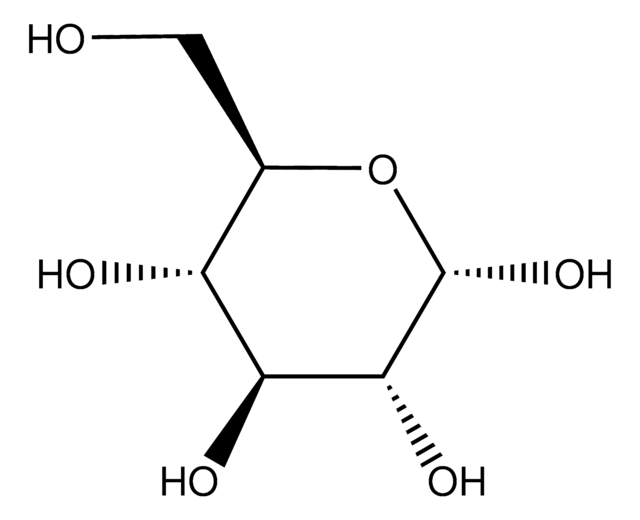
Maltodextrin
Sinonimo/i:
MLD
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
corn kernels
Livello qualitativo
Descrizione
dextrose equivalent 16.5 - 19.5
Stato
powder
Punto di fusione
240 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Stringa SMILE
O[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=O)[C@H](O)CO
InChI
1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h1,3-6,8-12H,2H2/t3-,4+,5+,6+/m0/s1
GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-SLPGGIOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- Formulation and characterization of catechin-loaded proniosomes for food fortification.: This study investigates the use of maltodextrin in the formulation of catechin-loaded proniosomes, highlighting its potential in food fortification applications. The results suggest significant benefits in terms of stability and bioavailability of catechins when encapsulated in proniosomes using maltodextrin (Shruthi et al., 2021).
- Impact of excipient choice on the aerodynamic performance of inhalable spray-freeze-dried powders.: This research explores how different excipients, including maltodextrin, affect the aerodynamic performance of spray-freeze-dried powders for inhalation. The findings emphasize the critical role of excipient selection in optimizing drug delivery efficiency (Wanning et al., 2020).
- Influence of spray drying on the stability of food-grade solid lipid nanoparticles.: The study examines the impact of spray drying on the stability of solid lipid nanoparticles, with maltodextrin serving as a stabilizer. The results indicate that maltodextrin effectively enhances the stability and shelf life of these nanoparticles in food applications (Salminen et al., 2019).
- The effect of binary mixture composition and magnesium stearate concentration on the Hiestand Tableting Indices and other related mechanical properties.: This article investigates the mechanical properties of tablet formulations, focusing on the role of maltodextrin in binary mixtures. The study provides insights into the optimization of tablet formulations for improved mechanical strength and performance (Likitlersuang et al., 2007).
- The 3D model: explaining densification and deformation mechanisms by using 3D parameter plots.: This paper presents a comprehensive model to explain the densification and deformation mechanisms in tablet formulations, using maltodextrin as a case study. The 3D parameter plots offer a detailed understanding of the compaction behavior of pharmaceutical excipients (Picker, 2004).
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Dmitri Simberg (University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, USA) reviews the used of dextran and cyclodextrin for the synthesis of nanoparticles used in drug delivery applications.
Dmitri Simberg (University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, USA) reviews the used of dextran and cyclodextrin for the synthesis of nanoparticles used in drug delivery applications.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.