440914
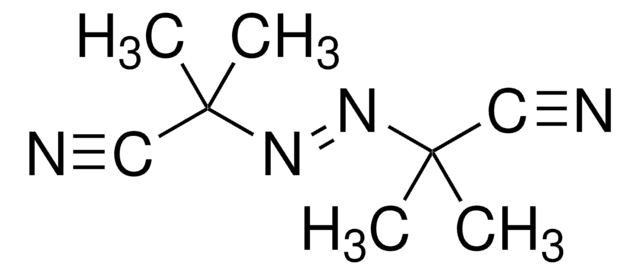
2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride
powder or granules, 97%
Sinonimo/i:
AAPH
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
97%
Stato
powder or granules
t1/2
10 hr(56 °C)
Punto di fusione
175-177 °C (lit.)
Solubilità
acetone, dioxane, methanol, ethanol, DMSO and water: soluble
Stringa SMILE
Cl.Cl.CC(C)(\N=N\C(C)(C)C(N)=N)C(N)=N
InChI
1S/C8H18N6.2ClH/c1-7(2,5(9)10)13-14-8(3,4)6(11)12;;/h1-4H3,(H3,9,10)(H3,11,12);2*1H/b14-13+;;
LXEKPEMOWBOYRF-QDBORUFSSA-N
Categorie correlate
Applicazioni
Polymerization initiator for acrylic, vinyl and allyl monomers.
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Self-heat. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
4.2 - Pyrophoric and self-heating hazardous materials
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Tools for Performing ATRP
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Applying ARGET ATRP to the Growth of Polymer Brush Thin Films by Surface-initiated Polymerization
We presents an article about Copper(I)-mediated Living Radical Polymerization in the Presence of Pyridylmethanimine Ligands, and the emergence of living radical polymerization mediated by transition metal catalysts in 1995, which was a seminal piece of work in the field of synthetic polymer chemistry.
Protocolli
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 440914-25G | 4061835515516 |
| 440914-100G | 4061835563098 |
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.