T6575
TOFA
≥98% (HPLC)
Sinônimo(s):
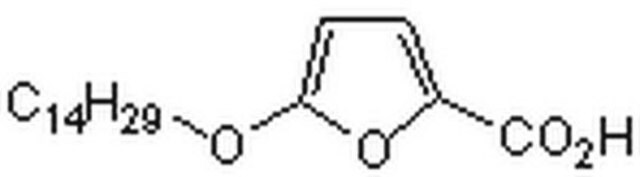
5-(Tetradecyloxy)-2-furoic acid
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Ensaio
≥98% (HPLC)
Formulário
powder
cor
white to beige
pf
112-115 °C
solubilidade
DMSO: 2 mg/mL, clear
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
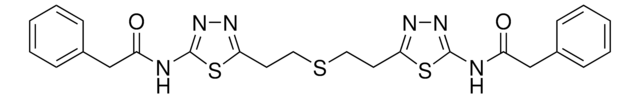
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCOc1ccc(o1)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C19H32O4/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-16-22-18-15-14-17(23-18)19(20)21/h14-15H,2-13,16H2,1H3,(H,20,21)
chave InChI
CZRCFAOMWRAFIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Aplicação
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Nota de preparo
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 2
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Information on fatty acid synthesis and metabolism in cancer cells. Learn how proliferatively active cells require fatty acids for functions such as membrane generation, protein modification, and bioenergetic requirements. These fatty acids are derived either from dietary sources or are synthesized by the cell.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica