SML0657
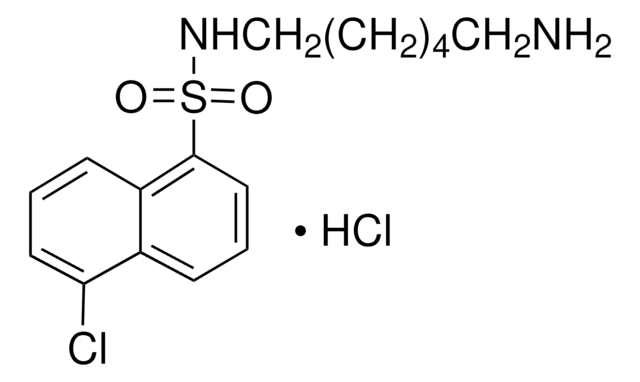
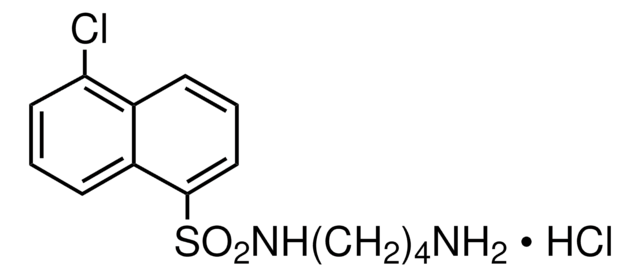
N-(6-Aminohexyl)-1-naphthalenesulfonamide hydrochloride
≥98% (HPLC)
Sinônimo(s):
W 5 hydrochloride, W-5 hydrochloride
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Ensaio
≥98% (HPLC)
Formulário
powder or crystals
cor
white to beige
solubilidade
H2O: 15 mg/mL, clear
temperatura de armazenamento
room temp
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
[S](=O)(=O)(NCCCCCCN)c1c2c(ccc1)cccc2.Cl
InChI
1S/C16H22N2O2S.ClH/c17-12-5-1-2-6-13-18-21(19,20)16-11-7-9-14-8-3-4-10-15(14)16;/h3-4,7-11,18H,1-2,5-6,12-13,17H2;1H
chave InChI
HOCSVIGHWPLMFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
Não está vendo a versão correta?
Se precisar de uma versão específica, você pode procurar um certificado específico pelo número do lote ou da remessa.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica