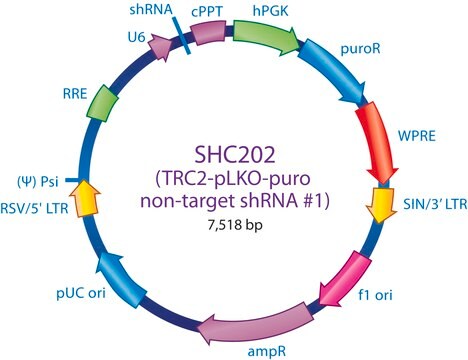
SHC202
MISSION® TRC2 pLKO.5-puro Non-Mammalian shRNA Control Plasmid DNA
Targets no known mammalian genes
Sinônimo(s):
MISSION® Control Vectors
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
linha de produto
MISSION®
concentração
500 ng/μL in TE buffer; DNA (10μg of plasmid DNA)
Condições de expedição
dry ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
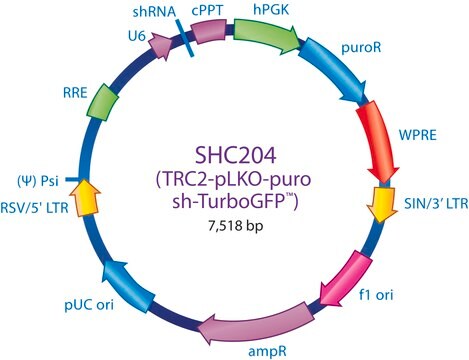
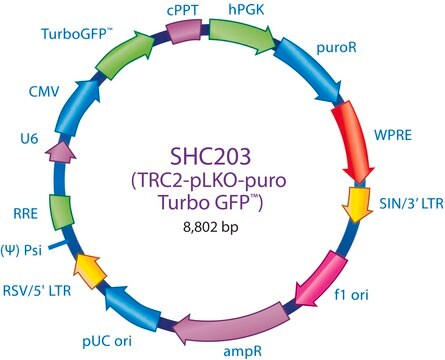
This shRNA non-mammalian control was designed using our Turbo GFP sequence and may cause some knockdown of tGFP. For maximum knockdown of tGFP, please refer to SHC004, SHC004V, SHC004H, SHC204, or SHC204V.
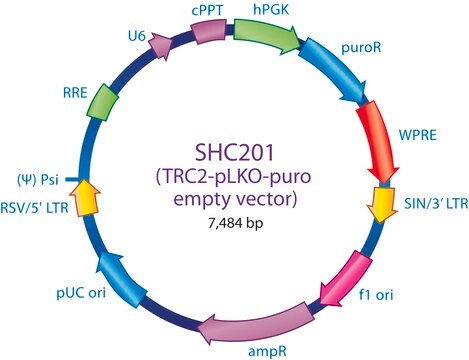
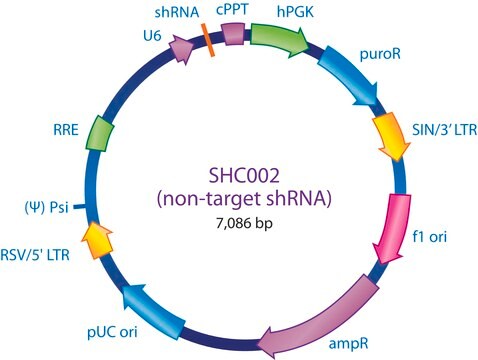
The MISSION® TRC2 Control Vector pLKO-puro Non-Target shRNA is a lentivirus plasmid vector. This vector is in the TRC2 pLKO-puro plasmid backbone, which contains the WPRE.
Ampicillin and puromycin antibiotic resistance genes provide selection in bacterial or mammalian cells respectively. In addition, self-inactivating replication incompetent viral particles can be produced in packaging cells (HEK293T) by co-transfection with compatible packaging plasmids (SHP001). The TRC2 Non-Target shRNA Control Vector is provided as 10 μg of plasmid DNA in Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer at a concentration of 500 ng/μl.
The MISSION® TRC2 Control Vector pLKO-puro Non-Target shRNA is a lentivirus plasmid vector. This vector is in the TRC2 pLKO-puro plasmid backbone, which contains the WPRE.
Ampicillin and puromycin antibiotic resistance genes provide selection in bacterial or mammalian cells respectively. In addition, self-inactivating replication incompetent viral particles can be produced in packaging cells (HEK293T) by co-transfection with compatible packaging plasmids (SHP001). The TRC2 Non-Target shRNA Control Vector is provided as 10 μg of plasmid DNA in Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer at a concentration of 500 ng/μl.
Aplicação
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) expressed from short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) are a powerful way to mediate gene specific RNA interference (RNAi) in mammalian cells. The MISSION® product line is based on a viral vector-based RNAi library against annotated mouse and human genes. shRNAs that generate siRNAs intracellularly are expressed from amphotropic lentivirus viral particles, allowing screening in a wide range of mammalian cell lines. In these cell lines, MISSION® shRNA clones permit rapid, cost efficient loss-of-function and genetic interaction screens. The vector contains an shRNA insert that does not target human or mouse genes, making it useful as a negative control in experiments using the MISSION® TRC2 shRNA library clones. This allows one to examine the effect of transfection of a short-hairpin on gene expression and interpret the knockdown effect seen with shRNA clones.
To see more application data, protocols, vector maps visit sigma.com/shrna.
Informações legais
Use of this product is subject to one or more license agreements. For details, please see http://sigmaaldrich.com/missionlicense.
MISSION is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
recomendado
Nº do produto
Descrição
Preços
Código de classe de armazenamento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Adaptor protein-3: A key player in RBL-2H3 mast cell mediator release.
da Silva EZ
PLoS ONE, 12(3), e0173462-e0173462 (2017)
Tianhe Huang et al.
Nature communications, 11(1), 2124-2124 (2020-05-03)
Penile squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC) accounts for over 95% of penile malignancies and causes significant mortality and morbidity in developing countries. Molecular mechanisms and therapies of PSCC are understudied, owing to scarcity of laboratory models. Herein, we describe a genetically
Lou-Ella M M Alexander et al.
Molecular immunology, 91, 8-16 (2017-09-01)
B cell activation is dependent on a large increase in transcriptional output followed by focused expression on secreted immunoglobulin as the cell transitions to an antibody producing plasma cell. The rapid transcriptional induction is facilitated by the release of poised
Succination is Increased on Select Proteins in the Brainstem of the NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 4 (Ndufs4) Knockout Mouse, a Model of Leigh Syndrome.
Piroli CG
Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 15(2), 445-461 (2016)
Ruben G de Bruin et al.
Nature communications, 7, 10846-10846 (2016-04-01)
A hallmark of inflammatory diseases is the excessive recruitment and influx of monocytes to sites of tissue damage and their ensuing differentiation into macrophages. Numerous stimuli are known to induce transcriptional changes associated with macrophage phenotype, but posttranscriptional control of
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica