H3917
Heparinase I and III Blend from Flavobacterium heparinum
lyophilized powder, stabilized with ∼ 25% (w/w) bovine serum albumin, ≥200 unit/mg protein (enzyme + BSA)
Sinônimo(s):
Heparinase I and Heparinase III blend
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
bacterial (Flavobacterium heparinum)
Nível de qualidade
conjugado
conjugate (Glucosaminoglycan)
Formulário
lyophilized powder
atividade específica
≥200 units/mg protein
concentração
≥200 unit/mg protein (enzyme + BSA)
Condições de expedição
dry ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
Descrição geral
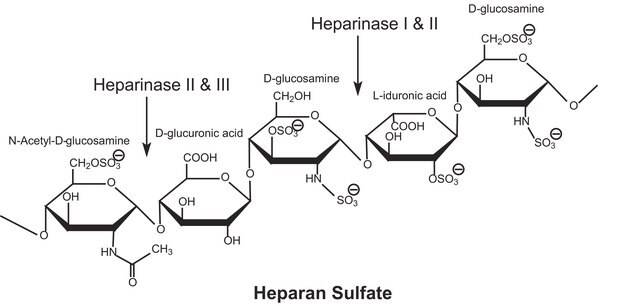
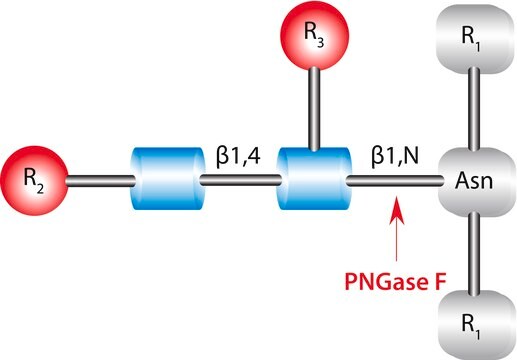
Heparinase is an inducible, non-extracellular heparin-degrading enzyme. Three types of heparinises are produced by Flavobacterium heparinum and contains specific sequences of heparin.
Aplicação
Heparinase I and III Blend from Flavobacterium heparinum has been used in:
- the digestion of heparan sulfate from ovine vitreous
- human embryonic kidney cells
- glycosaminoglycans from arterial tissues
- P0 retinae digestion
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Heparin-degrading lyase that recognizes heparin sulfate proteoglycan as its primary substrate.
Heparinase I and III plays vital role in various biological processes: modulate cell-growth factor interactions, cell-lipoprotein interactions, neovascularization. It cleaves highly sulphated polysaccharide chains in presence of 2-O-sulfated α-L-idopyranosyluronic acid and β-D-glucopyranosyluronic acid residues of polysaccharides.
Embalagem
Sold on the basis of Heparinase I units
Definição da unidade
One unit will form 0.1 micromole of unsaturated uronic acid per hour at 7.5 at 25 degrees C using Heparin, Sodium as substrate for heparinase I.
One unit will form 0.1 micromole of unsaturated uronic acid per hour at 7.5 at 25 degrees C using bovine kidney Heparan, Sulfate as substrate for heparinase III.
One unit will form 0.1 μmole of unsaturated uronic acid per hr at pH 7.5 at 25 °C. One International Unit (I.U.) is equivalent to approx. 600 Sigma units. Package sizes are sold in Sigma units.
One unit will form 0.1 micromole of unsaturated uronic acid per hour at 7.5 at 25 degrees C using bovine kidney Heparan, Sulfate as substrate for heparinase III.
One unit will form 0.1 μmole of unsaturated uronic acid per hr at pH 7.5 at 25 °C. One International Unit (I.U.) is equivalent to approx. 600 Sigma units. Package sizes are sold in Sigma units.
Outras notas
Enzyme Commission Numbers: 4.2.2.7 Hep I and 4.2.2.8 Hep III
Código de classe de armazenamento
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
S Ernst et al.
Critical reviews in biochemistry and molecular biology, 30(5), 387-444 (1995-01-01)
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) play an intricate role in the extracellular matrix (ECM), not only as soluble components and polyelectrolytes, but also by specific interactions with growth factors and other transient components of the ECM. Modifications of GAG chains, such as isomerization
Farizeh Aalam et al.
PLoS pathogens, 16(10), e1008968-e1008968 (2020-10-20)
Despite 25 years of research, the basic virology of Kaposi Sarcoma Herpesviruses (KSHV) in B lymphocytes remains poorly understood. This study seeks to fill critical gaps in our understanding by characterizing the B lymphocyte lineage-specific tropism of KSHV. Here, we
P M Galliher et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 41(2), 360-365 (1981-02-01)
Heparinase production by Flavobacterium heparinum in complex protein digest medium, with heparin employed as the inducer, has been studied and improved. The maximum productivity of heparinase has been increased 156-fold over that achieved by previously published methods to 375 U/liter
D A Chappell et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 268(19), 14168-14175 (1993-07-05)
Bovine milk lipoprotein lipase (LPL) induced binding, uptake, and degradation of 125I-labeled normal human triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by cultured mutant fibroblasts lacking LDL receptors. The induction was dose-dependent and occurred whether LPL and 125I-lipoproteins were added to incubation media simultaneously or
Cassandra R Blanchette et al.
PLoS genetics, 13(1), e1006525-e1006525 (2017-01-10)
The regulation of cell migration is essential to animal development and physiology. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans shape the interactions of morphogens and guidance cues with their respective receptors to elicit appropriate cellular responses. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans consist of a protein core
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica