43963
Moxalactam Supplement
suitable for microbiology
Sinônimo(s):
Listeria MOX Supplement
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
esterilidade
sterile
Nível de qualidade
Formulário
powder
prazo de validade
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
aplicação(ões)
environmental
food and beverages
microbiology
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
adequação
Listeria spp.
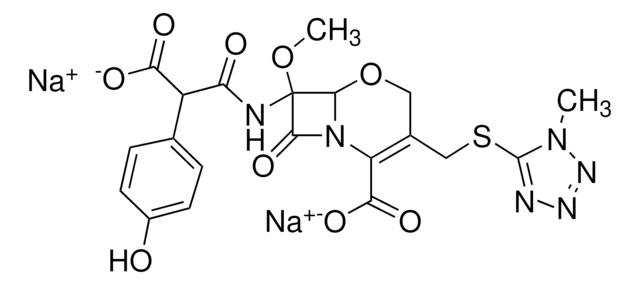
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
CO[C@]2(NC(=O)C(C(O)=O)c1ccc(O)cc1)[C@H]3OCC(CSc4nnnn4C)=C(N3C2=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C20H20N6O9S/c1-25-19(22-23-24-25)36-8-10-7-35-18-20(34-2,17(33)26(18)13(10)16(31)32)21-14(28)12(15(29)30)9-3-5-11(27)6-4-9/h3-6,12,18,27H,7-8H2,1-2H3,(H,21,28)(H,29,30)(H,31,32)/t12?,18-,20+/m1/s1
chave InChI
JWCSIUVGFCSJCK-CAVRMKNVSA-N
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Aplicação
Componentes
Moxalactam 20.0 mg
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica