764590
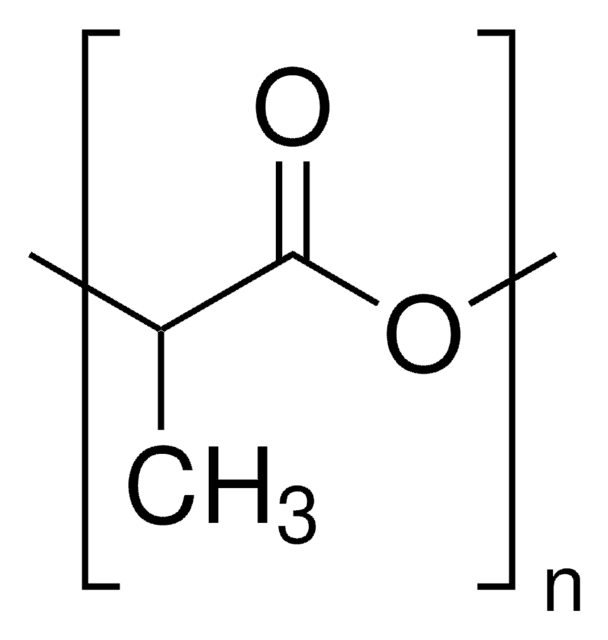
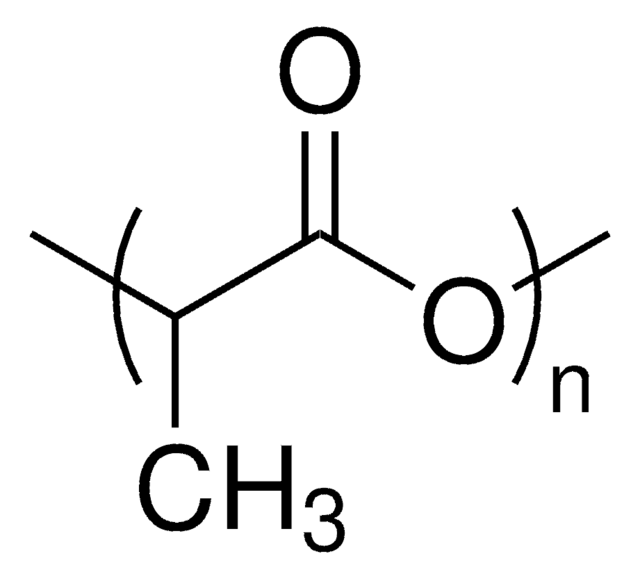
Poly(L-lactide)
average Mn 5,000, PDI ≤1.2
Sinônimo(s):
PLLA, Polylactide, L-Lactide polymer, PLA, Poly(L-Lactic acid)
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
forma
solid
Nível de qualidade
atividade óptica
[α]22/D -147°, c = 0.5% in chloroform
peso molecular
average Mn 5,000
prazo de degradação
>3 years
temperatura de transição
Tm 149-154 °C
PDI
≤1.2
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
Características e benefícios
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Professor Aran (Claremont University, USA) thoroughly discusses the engineering of graphene based materials through careful functionalization of graphene oxide, a solution processable form of graphene.
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
The world of commercial biomaterials has stagnated over the past 30 years as few materials have successfully transitioned from the bench to clinical use. Synthetic aliphatic polyesters have continued to dominate the field of resorbable biomaterials due to their long history and track record of approval with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica