About This Item
Produtos recomendados
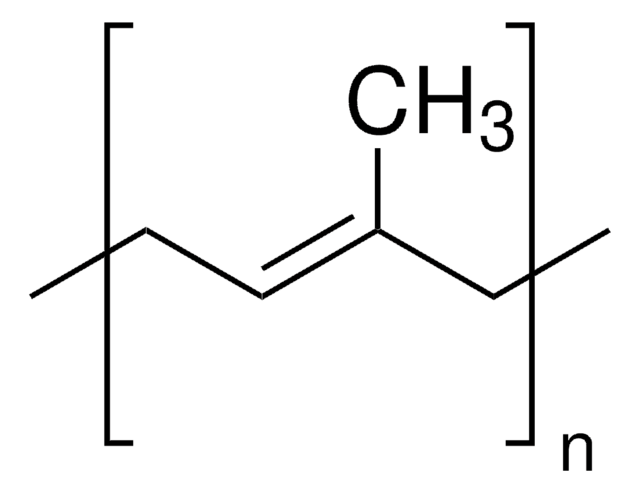
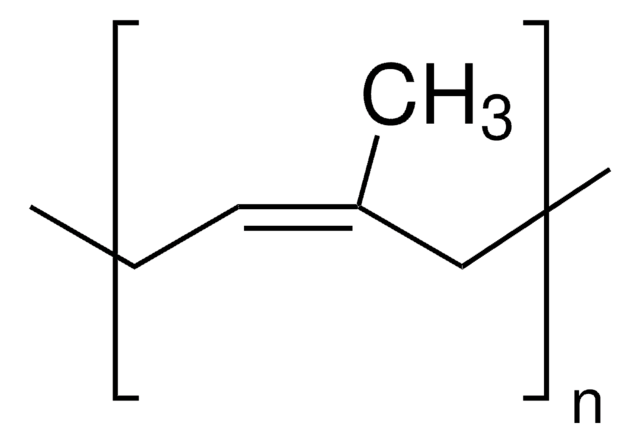
peso molecular
average Mw 60,000-70,000 (polyisoprene)
composição
solids, 27-29 wt. %
constante dielétrica
2.4
tensão superficial
29.2 dyn/cm
viscosidade
465-535 cP(25 °C)
p.e.
122-142 °C (lit.)
densidade
0.89 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
λmax
310-480 nm
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
O1C(OCC(C1)(C)C)CCCCCCCC
InChI
1S/C14H28O2/c1-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-13-15-11-14(2,3)12-16-13/h13H,4-12H2,1-3H3
chave InChI
UBZVSDZJBLSIJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Asp. Tox. 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Repr. 1B - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Órgãos-alvo
Respiratory system
Código de classe de armazenamento
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
75.2 °F - closed cup
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
24 °C - closed cup
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Protocolos
Negative Photoresist Procedure
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica