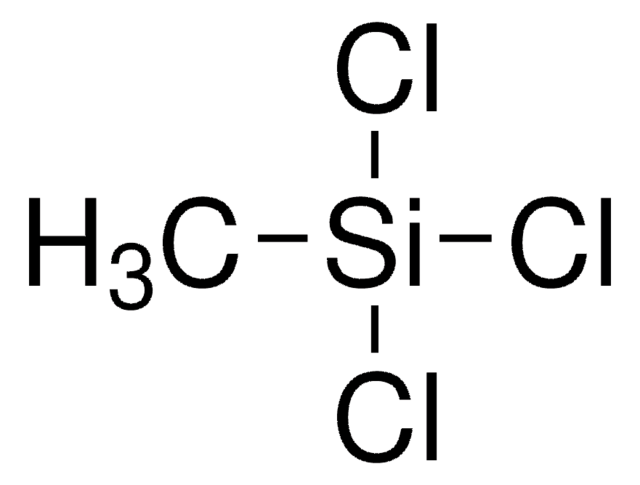440248
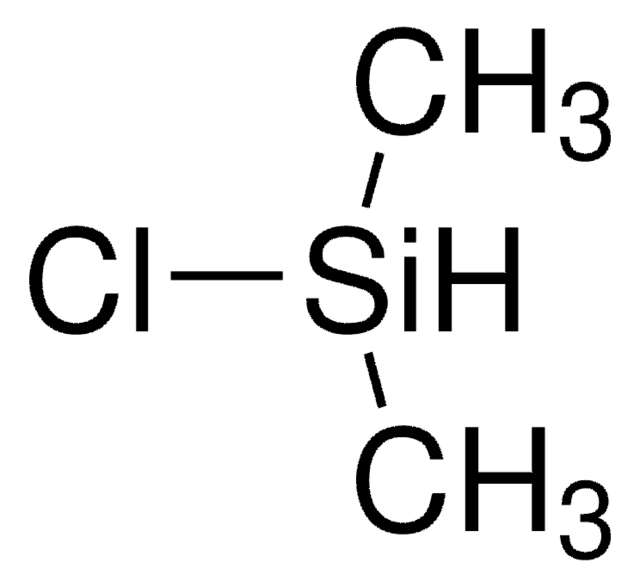
Dichloromethylsilane
≥97%
Sinônimo(s):
Methyldichlorosilane
About This Item
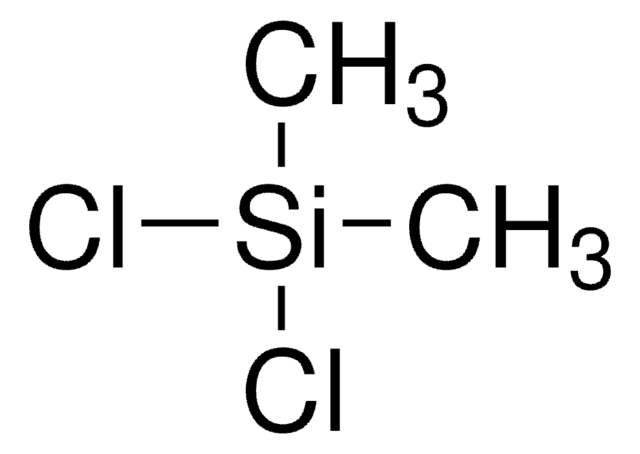
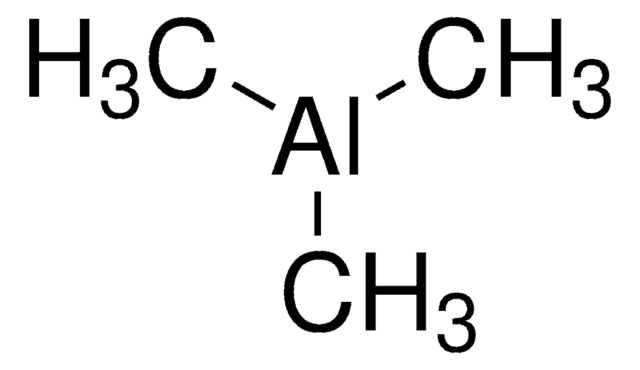
Produtos recomendados
densidade de vapor
4 (vs air)
Nível de qualidade
pressão de vapor
6.79 psi ( 20 °C)
Ensaio
≥97%
forma
liquid
temperatura de autoignição
471 °F
Lim. expl.
>55 %
índice de refração
n20/D 1.398 (lit.)
pb
41 °C (lit.)
pf
−93 °C (lit.)
densidade
1.105 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
C[SiH](Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/CH4Cl2Si/c1-4(2)3/h4H,1H3
chave InChI
NWKBSEBOBPHMKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- A General and Selective Synthesis of Methylmonochlorosilanes from Di-, Tri-, and Tetrachlorosilanes - Discusses a method for synthesizing Methylmonochlorosilanes, showing potential for varied applications in chemical synthesis (Y Naganawa et al., 2020).
- Polymerization of methylsilylenes into polymethylsilanes or polycarbosilanes after dechlorination of dichloromethylsilanes. - Investigates the polymerization of methylsilylenes, offering insights into the production of polymethylsilanes or polycarbosilanes from Dichloromethylsilanes (Y Tian et al., 2016).
- Synthesis of low viscosity of polymethylhydrosiloxane using monomer of dichloromethylsilane - Focuses on producing low-viscosity polymethylhydrosiloxane through hydrolysis-condensation of Dichloromethylsilane, significant for various industrial applications (VF Arini et al., 2022).
Embalagem
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Corr. 1A - Water-react 3
Perigos de suplementos
Código de classe de armazenamento
4.3 - Hazardous materials which set free flammable gases upon contact with water
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
-18.4 °F
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
-28 °C
Equipamento de proteção individual
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica