221015
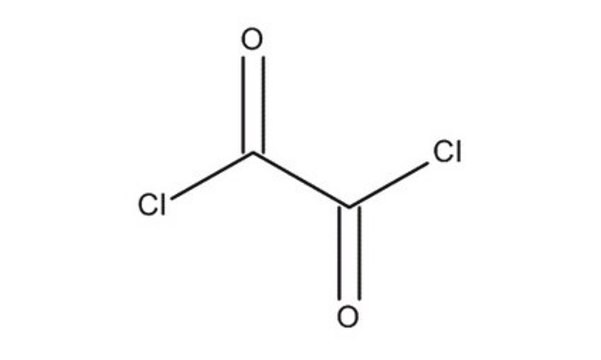
Oxalyl chloride
ReagentPlus®, ≥99%
Sinônimo(s):
Ethanedioyl dichloride
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
densidade de vapor
4.4 (vs air)
Nível de qualidade
pressão de vapor
150 mmHg ( 20 °C)
linha de produto
ReagentPlus®
Ensaio
≥99%
Formulário
liquid
adequação da reação
reagent type: oxidant
Impurezas
<10 ppb Heavy metals
cor
APHA: 0-150
índice de refração
n20/D 1.429 (lit.)
p.e.
62-65 °C (lit.)
pf
−10-−8 °C (lit.)
densidade
1.5 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
grupo funcional
acyl chloride
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
ClC(=O)C(Cl)=O
InChI
1S/C2Cl2O2/c3-1(5)2(4)6
chave InChI
CTSLXHKWHWQRSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- Preparation of Mosher′s acid chloride by reacting with Mosher′s acid in the presence of DMF.
- Activation of dimethyl sulfoxide for use in the oxidation of long-chain alcohols to carbonyls.
- Activation of α-keto carboxylic acids and N-heterocyclic carboxylic acids for alkynylation to form ynediones and N-heterocyclic ynones, respectively.
- Synthesis of N-heterocyclic ynones and ynediones, used to activate carboxylic acids
- Chlorination and halogenation
- Three-component [3+2] cycloadditions
- Reactions with organostannanes
- Synthesis of cyclopentenones
- Carbonylations, used as a carbonyl synthon
Embalagem
Informações legais
acessório
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Corr. 1B - Water-react 1
Perigos de suplementos
Código de classe de armazenamento
4.3 - Hazardous materials which set free flammable gases upon contact with water
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
51.8 °F - closed cup
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
11.0 °C - closed cup
Equipamento de proteção individual
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica