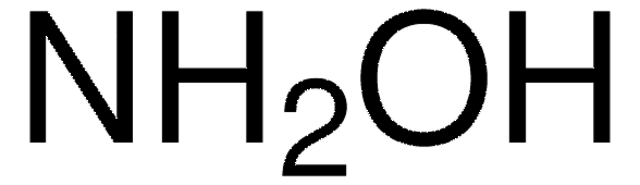194751
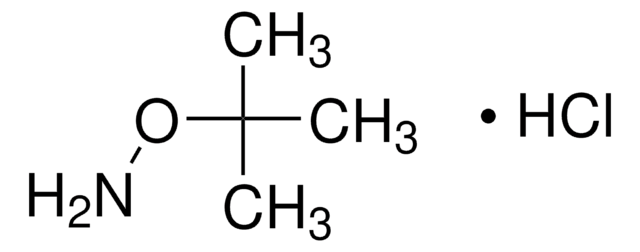
N-tert-Butylhydroxylamine hydrochloride
≥98%
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Fórmula linear:
(CH3)3CNHOH · HCl
Número CAS:
Peso molecular:
125.60
Beilstein:
3546053
Número CE:
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352100
ID de substância PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Produtos recomendados
Ensaio
≥98%
Formulário
solid
pf
183-185 °C (lit.)
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
Cl.CC(C)(C)NO
InChI
1S/C4H11NO.ClH/c1-4(2,3)5-6;/h5-6H,1-3H3;1H
chave InChI
DCSATTBHEMKGIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Aplicação
N-tert-Butylhydroxylamine hydrochloride was used in spin trapping of short-lived radicals. It was also used in the synthesis of α-ketoamides and 3-spirocyclopropanated 2-azetidinones.
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Yu-Kyung Kim et al.
Clinical hemorheology and microcirculation, 40(4), 315-324 (2009-01-08)
Irradiation has been shown to induce biochemical changes in stored red blood cells (RBCs) and to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). This study evaluated the hemorheological properties, the degree of lipid peroxidation and the oxidative susceptibility of irradiated RBCs. Furthermore
Hyun Jeong Kim et al.
Redox report : communications in free radical research, 10(6), 287-293 (2006-01-28)
Heat shock may increase oxidative stress due to increased production of reactive oxygen species and/or the promotion of cellular oxidation events. Therefore, compounds that scavenge reactive oxygen species may regulate heat shock-induced cell death. Recently, it has been shown that
Jin Hyup Lee et al.
Carcinogenesis, 25(8), 1435-1442 (2004-03-16)
Exposure of cells to ionizing radiation leads to formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are associated with radiation-induced cytotoxicity. Therefore, compounds that scavenge ROS may confer radioprotective effects. Recently, it has been shown that the decomposition product of the
David W Killilea et al.
Antioxidants & redox signaling, 5(5), 507-516 (2003-10-29)
Iron accumulates as a function of age in several tissues in vivo and is associated with the pathology of numerous age-related diseases. The molecular basis of this change may be due to a loss of iron homeostasis at the cellular
On the anti-aging activities of aminoguanidine and N-t-butylhydroxylamine.
A R Hipkiss
Mechanisms of ageing and development, 122(2), 169-171 (2001-02-13)
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica