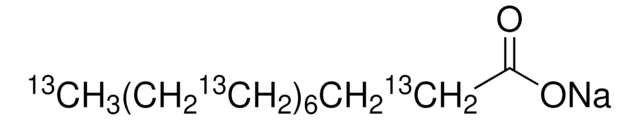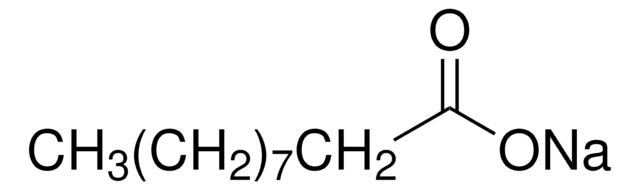Key Documents
P9767
Sodium palmitate
≥98.5%
Synonim(y):
Hexadecanoic acid sodium salt, Palmitic acid sodium salt
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
plant (palm)
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥98.5%
Postać
powder
mp
283-290 °C (lit.)
grupa funkcyjna
ester
typ lipidu
saturated FAs
Warunki transportu
ambient
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
ciąg SMILES
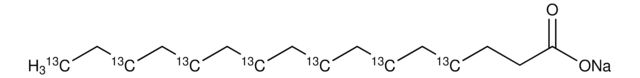
[Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C16H32O2.Na/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16(17)18;/h2-15H2,1H3,(H,17,18);/q;+1/p-1
Klucz InChI
GGXKEBACDBNFAF-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Zastosowanie
- to induce inflammation and thrombosis pathway in murine macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 cell line by activating reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, Janus-kinase (JNK) signalling and release of histone H3 by western blotting and cell viability by MTT assay
- to induce lipogenesis in AML12 cells and primary hepatocytes to analyse the effect of irisin on PA induced lipogenesis and related signal pathways by western blot analysis and quantitative PCR analysis
- as a component in free fatty acid mixture to induce cellular steatosis in HepG2 cell lines and determination of lipid accumulation by Oil-Red-O staining
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Information on fatty acid synthesis and metabolism in cancer cells. Learn how proliferatively active cells require fatty acids for functions such as membrane generation, protein modification, and bioenergetic requirements. These fatty acids are derived either from dietary sources or are synthesized by the cell.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej