Kluczowe dokumenty
P2153
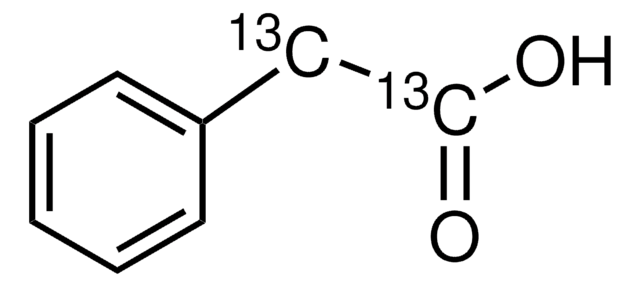
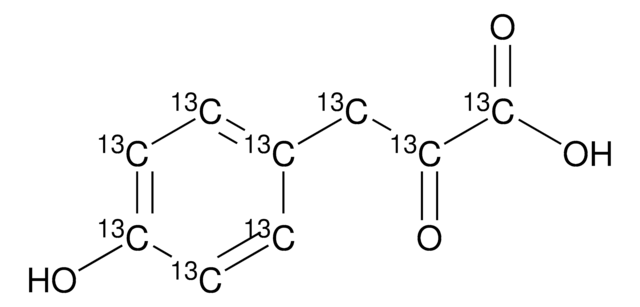
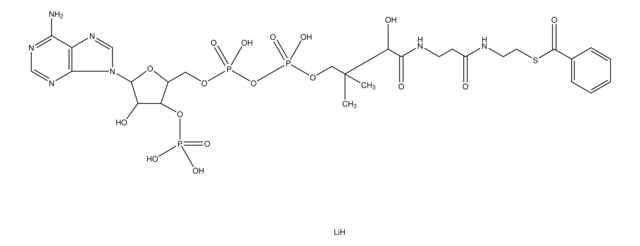
Phenylacetyl coenzyme A lithium salt
~95%
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Próba
~95%
Formularz
powder
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
ciąg SMILES
[Li].CC(C)(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OCC1OC(C(O)C1OP(O)(O)=O)n2cnc3c(N)ncnc23)C(O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCSC(=O)Cc4ccccc4
InChI
1S/C29H42N7O17P3S.Li.H/c1-29(2,24(40)27(41)32-9-8-19(37)31-10-11-57-20(38)12-17-6-4-3-5-7-17)14-50-56(47,48)53-55(45,46)49-13-18-23(52-54(42,43)44)22(39)28(51-18)36-16-35-21-25(30)33-15-34-26(21)36;;/h3-7,15-16,18,22-24,28,39-40H,8-14H2,1-2H3,(H,31,37)(H,32,41)(H,45,46)(H,47,48)(H2,30,33,34)(H2,42,43,44);;
Klucz InChI
BYSZOQQABOXIQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Zastosowanie
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej