Kluczowe dokumenty
39246
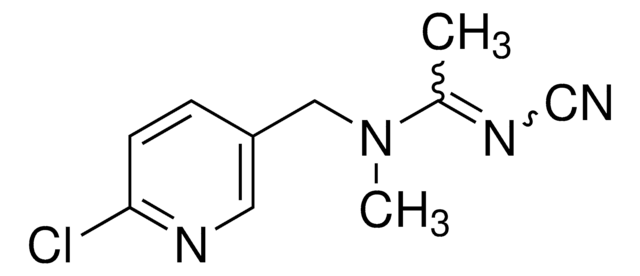
Acetamiprid-d3
PESTANAL®, analytical standard
Synonim(y):
(E)-N-(6-Chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-N′-cyano-N-(methyl-d3)acetamidine
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
analytical standard
Poziom jakości
czystość izotopowa
≥99.0 atom % D
linia produktu
PESTANAL®
Próba
≥98.0% (HPLC)
okres trwałości
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
metody
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
Zastosowanie
agriculture
Format
neat
przesunięcie masy
M+3
ciąg SMILES
[2H]C([2H])([2H])N(Cc1ccc(Cl)nc1)\C(C)=N\C#N
InChI
1S/C10H11ClN4/c1-8(14-7-12)15(2)6-9-3-4-10(11)13-5-9/h3-5H,6H2,1-2H3/b14-8+/i2D3
Klucz InChI
WCXDHFDTOYPNIE-WZAFYLDHSA-N
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
see also 46451
Zastosowanie
Opakowanie
Informacje prawne
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Protokoły
Learn more about Neonicotinoids - active substances used in plant protection products to control harmful insects.
On Friday, April 27, 2018, the European Union decided to ban the use of three neonicotinoid insecticides from use on field crops, having deemed them dangerous to bees. This application demonstrates the analysis of these banned compounds and others from dandelion blossoms using QuEChERS and LC-MS.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej