17774
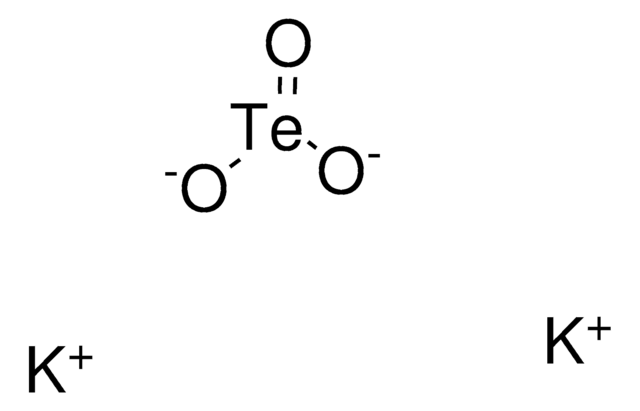
Potassium tellurite solution
1% in H2O, suitable for microbiology
About This Item
Polecane produkty
agency
according to ISO 6888-1:2020
Poziom jakości
sterylność
sterile (Filtered and Aseptic Handled)
Postać
liquid
okres trwałości
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
stężenie
1% in H2O
Zastosowanie
environmental
food and beverages
microbiology
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
przydatność
Corynebacterium spp.
Staphylococcus spp.
ciąg SMILES
[K+].[K+].[O-][Te]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/2K.H2O3Te/c;;1-4(2)3/h;;(H2,1,2,3)/q2*+1;/p-2
Klucz InChI
BFPJYWDBBLZXOM-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Zastosowanie
Inne uwagi
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Chromogenic media enable the selective detection of S. aureus, which produce bluish-green colonies that are clearly differentiated from other species.
Podłoża chromogenne umożliwiają selektywne wykrywanie S. aureus, które wytwarzają niebiesko-zielone kolonie, wyraźnie odróżniające się od innych gatunków.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej